Functions of Marketing

A marketing function is a specialized activity performed in delivering the goods and services that consumer’s need. In other words, marketing functions are the activities that bridge the distance, time and possession gaps in an exchange relationship.
Planning function
These functions are performed to prepare the plans of various marketing activities. These are helpful in carrying out the other marketing functions
1. Marketing information and research
Marketing decisions can be no matter then the information upon which they are based. Marketing information includes all facts, estimates, opinions, and figures used in marketing decisions that affect the exchange of goods and services. Marketers need various information regarding products, price, demand, market competition, middlemen, selling methods and other elements of marketing mix.
2. Consumer analysis
This is an important function of marketing. Under this function, the marketing department examines and evaluates consumer characteristics, needs, tastes, lifestyles and purchase processes. It is concerned with the decisions and acts of individuals in buying and using products. Marketers study buyer behavior to learn what consumers are like and the reasons behind their purchases.
3. Product planning and development
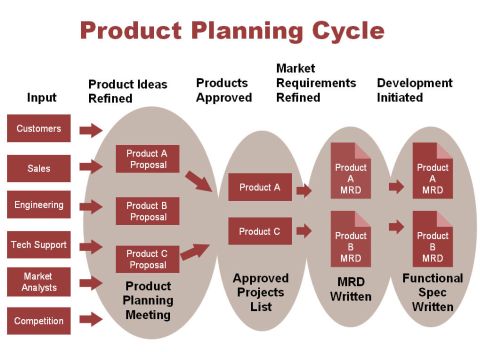
This function is a systematic decision making pertaining to all aspects of a firm’s product. A product serves as an instrument of achieving marketing objectives. Product planning g determines the characteristics of products, which best meet the consumer’s numerous desires that add saleability to products. It allows the firm to pinpoint opportunities, develop marketing programs and maintain successful products.
4. Distribution planning
The function involves systematic decisions making regarding the physical movement and transfer of ownership of a product from producer to consumer. It includes transportation, storage, and customer transactions. Distribution functions are carried out through a channel of distribution, which is comprised of wholesalers, retailers, and other middlemen.
5. Standardization and grading
These marketing functions involve setting up of standards or specifications of a product and maintaining those standards during the period for which they are effective. It is to determine basic limits to classes of products. In the light of such prescribed standards or norms, the goods can be divided or sorted out into a number of groups or lots.
6. Product branding
Branding is an act of giving a specified name, design, or symbol to a product from one seller. When brand names, brand marks or trade characters are registered, they become trademarks. When developing a brand, a firm needs to state its branding philosophy. Branding has several uses. Product identification is eased. Product prestige increased.
7. Packing and packaging
These have become specialized functions in recent years. Goods are packed in suitable containers to protect them from spoilage, breakage, leakage, etc. damage to goods generally occurs either in the course of their transportation or during the time when goods are lying in the warehouse. Packing, on the other hand, is concerned with putting articles on the market in convenient size lots. It is putting the goods in tins, bottles, boxes, cans, bags, and barriers or other containers of such convenient size as can easily be handled by the buyers.
8. Financing
Financing is an ancillary but important function of marketing. It facilities the process of marketing activities. It is providing the financial resources to produce, transport, store, promote, sell, and buy goods or services. A firm uses funds to finance the marketing agencies in their various activities. It also needs the financing of goods moving into and through the channels of distribution.
9. Marketing management
for each area of marketing, the managerial aspect is important. Marketing has the diversity of problems, a marketing manager must deal with. Managers plan, organize direct, staff, and control marketing programmes. the marketing manager has to coordinate all the work of a marketing department.
Exchange functions
The exchange is at the heart of all the marketing and transfer of ownership is the primary objective of the marketing process. Hence, the performance of exchange functions assumes high importance. These are described below;
1. Merchandising
Merchandising includes all company planning activities aimed at developing products and to meet a market demand. It is the procedure whereby companies plan for products that are to be marketed. It is knowing what the customers want and getting the right product to the right market, at the right time, at the right price and at the right place.
2. Buying and assembling
Buying is one of the fundamental functions of marketing. In fact, it is the first step in the process of marketing. It is performed by all marketers. It refers to the planning of purchase, selection of goods to be sold or to be used in business, assembling of goods in right quantity, at the right time and at the right place. Assembling is important to aid in selling goods. good are assembled mainly for two purposes: to meet the demands of the buyers and to provide a sufficient volume of business to a middleman.
3. Selling

The primary objective of marketing is to sell goods and services at a profit. All marketing efforts revolve around the selling process. This is probably the most visible function of marketing. It is the process whereby goods and services finally flow to the consumers who need them. It involves promoting the product. It includes the use of personal selling, advertising, and other mass selling methods.
Distributing functions
These functions facilitate the physical movement of goods from the place where they are produced to those where they are to be consumed. These are described below;
1. Transportation
Transportation is a physically flow of goods that occurs in marketing channels. It is moving goods from one geographical location to another. It means moving products through time and space. It is concerned with efficiently delivering raw materials, parts, semifinished items, and finished products to designated places, at designated times, and in proper condition.
2. Storage
Storage is another distributing function of the marketing process. It means retaining the goods in a perfect state until buyers want them. Storage provides time utility to products. It helps firms to hold and preserve the stock of goods for different periods of time during the marketing process. With the help of storage and warehousing, a marketer can easily equalize and regulate the distribution of goods place-wise and time-wise so that supply can be adjusted with changing demand in business.
3. Risk-bearing
The risk is present in all marketing transactions. The risk in marketing means uncertainty in regards to cost, loss or damage. It is a loss arising on account of unforeseen causes such as fluctuations in prices, changes in fashion and attitudes of consumers or breakage. A firm can never be sure that customers will want to buy its products. Products can also be damaged, stolen, or outdated. changes in income, the appearance of substitute products, newer methods of sales promotion, etc. may also create risk.
Need Help with Your Assignment?
Get expert guidance from top professionals & submit your work with confidence.
Fast • Reliable • Expert Support
Upload NowOther Assignments