- support@locusassignments.com
Unit 14 Tour Operator Industry Assignment

|
Program |
Diploma in Travel and Tourism |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 14 Tour Operator Industry |
|
QFC Level |
Level 5 |
Introduction
This unit 14 tour operator industry assignment revolves around the discussion of understanding the tour operator industry in the sector of travel and tourism. The discussion starts with the development of the tourism industry with the study of effects of recent trends on its development. The unit argues about the stages that have been involved in the formation of the tour package and the factors that affect various decisions. The unit also focuses on the strategic as well as the tactical decisions that have been made by the operators in order to survive in the industry and to compete with the competitors.

Task 1
LO1. Understand the tour operators industry within the travel and tourism sector.
P1.1 Analyze the effects of current and recent trends and developments on the tour operators industry.
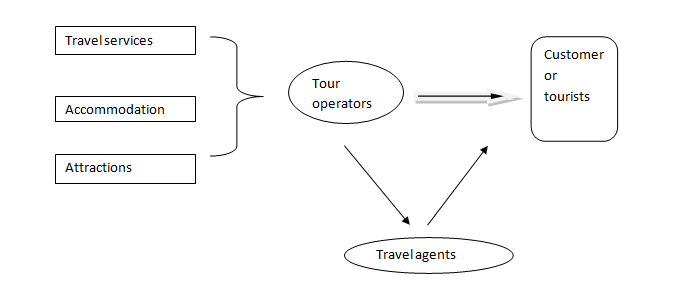
Tourism refers to travelling for pleasure. It involves the business that attracts and entertains people or tourists who travels round the world with different objectives. Operating tours is the main activity that needs to be conducted in this business of tourism. Tourism is majorly divided into two types, domestic and international. Domestic tourism is about the tours that have been conducted in the native country and international tourism involves tours worldwide. International tourism has been affected by many international as well as domestic factors. The most important element of tourism is the tour operator. They are the organisations that combine the tour and tourism in a specific package. The package may include travelling, hotels, sightseeing etc. These organizations develop different packages according to the tourists and the places that need to be visited. Some of the packages are customized according to the choice of the customers.
Types of tour operators
There are majorly four types of tour operators. The below classification of the tour operators have been done according to the processes they used to conduct in the tourism industry.
- Inbound tour operators: Inbound tour operators are those who fulfil the tourism needs of the foreign tourists into the country. These operators focus on providing services to the foreign tourists from their arrival to their departure from the country. They provide services like accommodation, food, travelling, sightseeing, travel guides, entertainment etc. Sometimes, inbound operators collaborate with some of the foreign tour operators and form the holiday packages for the tourists. Inbound tour operators play very important role in building the image of the country by commercialising the tourist resources to raise the earnings of the country by tourism. (Cobb, 2003). GTi travel group is one of the leading inbound tour operators in UK that mainly focuses on providing group travel services to the tourists.
- Outbound tour operators: These operators form the packages for the tourists of their own country. They market and sell the packages that deals with the trips of sending own people to foreign country. The outbound tour operators collaborate with the inbound tour operators of another country to provide all the tourism services like transportation, accommodation, travelling etc to the individual or group of people in the foreign country they are visiting. They act as the intermediary between the operators of the foreign country and the tourists. They generally do not contribute in foreign exchange earnings, as they do not sell the packages to the foreign tourists. (Moore and Doherty, 2011) “My travel” and “First Choice” are two of the leading outbound tour operators in UK.
- Domestic tour operators: Domestic operators operate in the boundary of their own country. They sell their packages to the native individuals or group of people who wants to travel inside the country borders. Most of the tour operators focus on international tourisms because of high returns and margins but they are now introducing some of the packages for the domestic travellers to enhance the domestic tourism as well as to promote the national integrity of the country. Leisure Breaks is one of the domestic tour operators in UK that facilitates the local people or group of people with the tourism services all over their tour.
- Specialist tour operators: There are the operators that design special tour to the people or group of people according to their choices. They have variety of packages for the untouched destinations. These are also known as tailor made operators because they modify the tours according to the preference of tourists regarding location, accommodation, food, transport etc. They are the most knowledgeable operators among all as they have the in depth knowledge of all the facilities available at different tourist destinations of every range. They design the tours with mix and match of these facilities according the tourist’s budget and choice. (Page and Connell, 2010)
Long travel is one of the leading UK based specialist tour operator that has customer centred approach. This approach allows them to tailor the holiday package according to the customer’s preference regarding the location, services, facilities, style, character, accommodation etc. (Sigala, Chritou and Gretzel, 2012)
Role of tour operators: The major role of these tour operators is to act as the intermediaries between the tourism services and the end customers.
Major tour operators in UK: There are four major tour operators in UK that mainly keeps their focus on international tourism as this industry has high margin and high returns in terms of monetary profits. This also helps to build the image of the country worldwide and allow more foreign exchange. (Walker and Hrading, 2007)
1. TUI AG: This is one of the leading operators in UK that facilitates international tourism to raise the standards of tourism industry.
- Origin: Germany
- Annual revenue: 23.8 billion Euros
- Operating countries: 15 European countries
- Ownership: 81 tour operators
2. My Travel PLC: This is the second leading tour operators and this concentrates on international tourism and falls under the category of outbound operators.
- Origin: UK
- Annual Revenue: 8.2 billion Euros
- Operating areas: UK/Ireland, North America, Northern Europe, Germany, Austria, and Switzerland.
- Ownership: 39 tour operators
3. Thomas Cook AG
- Origin: Germany
- Annual revenue: 8 billion Euros
- Operating areas: Germany, UK, Ireland, France, Austria, Hungary, Poland, Slovakia, Slovenia, Egypt, India, and Canada
- Ownership: 30 tour operators
4. First Choice:
- Origin: UK
- Annual revenue: 3.8 billion Euros
- Operating areas: France, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, Austria, Switzerland, UK, Ireland, and Canada
- Ownership: 28 tour operators
Market share of some of the UK based operators:
The above figure suggests that Thomson has the largest share of market of tourism industry in UK followed with Airtours, Thomas Cook and First Choice. (Goretti Sanches Lima, 2013)
Number of visitors in UK
This figure shows total number of bednights by international tourists in different cities of UK. This determines the trends of number of tourists in UK.
Contact us
Get assignment help from full time dedicated experts of Locus assignments.
Call us: +44 – 7497 786 317Email: support@locusassignments.com
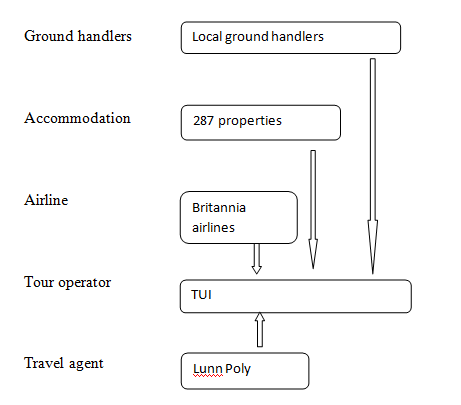
Vertical integration: Vertical integration refers to collaboration or investment in the associated business at different levels. In terms of tourism industry, when tour operators invest or collaborate with the service providers like transport companies and hotels is known as backward vertical integration and if they invest in acquiring travel agencies then it is known as forward vertical integration. TUI is one of the leading tour operators in UK that focuses on vertical integration of the business. Below diagram shows the forward and backward integration of TUI.
Horizontal integration: Horizontal integration involves merging of companies in the same industry to remove competition. In 1995, UK based tour operator Thomas Cook has took over another company called Sunworld to raise its standard in the company by acquiring more market share and by competing with the competitors. (Koenig-Lewis and Bischoff, 2010)
Changing trends in holiday
- Customisation: Customisation refers to the modification in the tour packages according to the preferences. Earlier, tour packages was restricted to standardised forms and is designed by the operators with influence of some other factors like government and tourism service providers. Now, the time has changed. Some of the specialised tour operators design the tour packages according to the preferences of location, accommodation, transport etc by the customers.
- Vertical integration: Tour operators have increased the range of the products in the tour packages to facilitate the customers or tourists. Horizontal and vertical integration are the practices that have been conducted by the operators to widen their product range. (Nikraftar and Hosseini, 2016)
- Responsible tourism: Responsible tourism involves the removal of the negative effects of tourism and maximisation of the various benefits that can be earned by tourism. Responsible tourism results in the benefits of the host community by enhancing their well-being. It involves environment conservation, economic vitality and cultural awareness.
Role of different trade bodies in tourism:
- ABTA: It is the largest travel association in UK and provides expertise and advice to the holidaymakers over the packages they design. They also help the operators to resolve the issues that may generate during the travel and tourism business.
- AITO: Association of independent tour operators represents around 122 operators in Britain. They provide assistance and specialisation to the independent and specialised tour operators.
- FTO: Federation of tour operators is the organisation that coordinates the tourism activities between the countries. It is merged with ABTA in 2008.
- UK CAA: The Civil Aviation Authority frames the policy and regulates the aviation industry. It is a public organisation formed by the government of UK.
Task 2
LO2 Understand stages involved in creating holidays:
P.2.1 Assess the stages and timescales involved in developing holidays
Planning is very necessary in the tourism industry. It is necessary for the tour operators to plan the activities in orderly basis to make a tour package that can attract the tourists. There are many stages involved in planning. These stages need to be practiced in orderly manner to come up with an effective tour package plan.
- Market research: Market research involves the overall research of the industry as well as the environment to fetch out whether the product that has been generated is worth or not. Market research involves economic research that deals with the knowledge of the economy of the country that has been visited with the economy knowledge of the host country as well. Another types of the researches that have been involved in this section are demand supply research, product research, customer and competitor research and sales research. (Clarke, 2010)
- Planning and scheduling: This stage involves the planning and decisions regarding the location of the tour, accommodation, travelling dates, group size, amenities, and attractions to be visited etc need to be taken. Proper scheduling of the activities has been done in this stage.
- Contracting: This stage involves the framing and signing of the agreements between the tour operators and the service providers. Some of the contracts need to be signed with the tourists also. This is a legal issue and needs to be done on time without any mistakes.
- Costing: This stage involves the overall costing of the package tour. The costing should be done according to the activities involved in the tour package. The costing consists of travelling tickets, accommodation and food, pick and drop fees, guides, entry fees of the attractions etc. (Moore and Doherty, 2011)
- Financial evolution and pricing: Evolution and pricing involves the action of calculating the expenses and profit margins by involving all the price fluctuations. This determines the profit of the operators. (Goretti Sanches Lima, 2013)
- Tour brochure: Formation of brochure is very important to create awareness about the tour among the population. The brochure should be such that attracts the customers and should provide with all the basic and important information of the package.
- Advertising: Different methods can be used to advertise about the tour among the population. These methods include TV, radio, newspapers, internet etc.
- Operations and execution: This stage involves the steps like deposits, ticket bookings, itinerary checklists etc. This stage is very important as it deals with the practical implementation of the actions for planning a tour.
- Post tour management: This stage comes after the completion of the tour. This involves taking the feedback from the people associated with the tour to make improvement in the next. This also involves the payment that is due to the service providers.
According to the case, the planning of the tour for students requires some of the stages like market research to decide the destinations and accommodations. Planning and scheduling needs to be done for proper management of the student’s tour. Contracts need to be signed with the university and with the hotels and flight providers for the bookings.
P2.2 Evaluate the suitability of different methods of contracting for different components of the holiday and different types of tour operator.
In general terms contracts are the agreements that have been signed by the two parties when they agrees on the conditions of the contract. In terms of tourism industry, contractual relationship between the tour operators, service providers and the tourists is very important. There are different types of contracts that need to be signed by the associated parties to safeguard themselves from the legal issues related to travel and tourism. (earth-net., 2013).
- Fixed contracts: Fixed contracts involve the conditions about the prior bookings that have been done for the tourists.
- Allocation contract: This contract is done between the hotelier and the tour operator. In this contract, information regarding the booking of the beds in the hotel is communicated to the hotelier so that he can sell rest of the rooms. This contract is also signed in order to book the seats in the flights.
- Ad-hoc contracts: These contracts deal with overbooking or extra arrangements of the seats or the beds. These contracts have mostly signed by the tailor made operators to arrange the services for their customers.
- Charter flights: These are the special flights paid by the companies for the holidaymakers to travel. The seats are not offered to the public. (Walker and Harding, 2007)
In the above case, fixed contracts method of contracting has been used to do the prior booking of hotels and flights.
P2.3 Calculate the selling price of a holiday from given information.
The destination of the student’s tour has been decided as Greece. The tour is of 7 days and the family members of the students are also allowed to come with them but the prices vary accordingly with the age of the family member. The hotel that has been booked is Avra Beach Resort with twin sharing rooms for 80 people. The prices for the activities have been discussed below: (Walker and Harding, 2007)
7 days tour package for Greece:
|
facilities |
Price (in pounds) |
||
|
Students |
Guest (above 10 years) |
Guest (6 months-10 yrs) |
|
|
Accommodation
|
30 |
42 |
21 |
|
Transport Air tickets Taxi and coach fare Visit fare |
102.2 37.2 50 |
143.08 52.08 70 |
71.54 26.04 45 |
|
Food
|
15 |
21 |
10.5 |
|
Sightseeing and entry tickets
|
30 |
42 |
21 |
|
total |
264.4 |
370.16 |
185.08 |
Task 3
LO3 Be able to review brochures and methods of distribution used to sell holidays
P.3.1- Evaluate the planning decisions taken for the design of a selected brochure.
A brochure is a template or a publication that is designed by the tour operators in order to attract their target audience to opt for that tour package. It is the way to advertise about the tour package that has been introduced by the operator. There are many purposes of designing brochures. It helps the operators to communicate about the tour packages to the people. It allows the operators to convey the relevant information regarding the package and also helps the tour operator organisation to build their image in the market. The brochure helps the customers to know about the company’s position and reliability. (Page and Connell, 2010) The planning decisions that have been taken regarding the formation of a brochure include:
- Design: The design of the brochure is about the layout and the artwork that has been used to make the brochure attractive. The large companies hire Ad agencies to design their brochures. The purpose of the brochure decides the design of the same.
- Cost: The first element that has been considered in the cost is the budget of the operator. The cost of the brochure includes the expenses in printing, designing, paper use, distribution media etc. (Nikraftar and Hosseini, 2016)
- Format: Format of the brochure involves the writing style, font size, colour, front cover, contents etc. Theme is the basic message that needs to be given to the people. This content of the whole brochure is related to this big and single theme message. Brochure folds determine the opening of the brochure. The brochure should be folded in such a way that it opens with the orderly message. Paper selection is about the type and the colour of the paper. This should complement the message that needs to be conveyed by the brochure. Photos and graphics provide the visual treat to the customers. It is critical to make the selection regarding the photos and graphics on the brochures and this has a great impact on customer’s mind.
- Target market and budget: Identifying the target market and budget helps in determining the type of brochure that has been used.
- Print specifications: Print specifications involve the decisions regarding the type of the print that has been used in terms of colour schemes.
Timescale and stage of production: The type of the brochure that has been used also depends on the stage of production. If the business is new and is at introductory stage then it used to introduce a brochure that is more attractive while the already existing business needs to introduce the brochures that are full of information. (Thomascook.com., 2016)
P3.2 Asses the suitability of alternatives to a traditional brochure for different types of tour operators and recommend the most appropriate for your tour package.
With the advancement in the technology, it has been observed that many traditional methods of marketing have lost their identity. Brochures are one of them. Many new methods of advertising and communication have been introduced to replace the brochures. Some of them are discussed below:
- Press: Press involves the print media. More and more population have access to newspapers and magazines, so this medium of information sharing is easy to reach up to large masses.
- E- brochures: E- brochures are the electronic brochures that are available online. This method of communication is the easiest way to reach to the people, as it does not require any extra efforts of distribution. Use of internet is common these days and so access to these E-brochures. (Thomascook.com., 2016)
- Social media: It is the most inexpensive method that can replace the traditional brochures technique. It is a promotional tool that has took over the position of direct marketing and serves the purpose of providing special offers to the people.
- Leaflets/flyers: These are the single page advertisement that has been conducted at last minute to provide brief information of the product to the limited audience.
- Business events/ Exhibitions: This method of advertising is used to target the potential customers in large masses. These events provide opportunities to make business contacts that can help in framing good relationship and image in the market.
- Outdoor media: Outdoor media refers to the advertising that can be done on buses, public billboards, walls etc. This method helps the companies to create awareness about the product among public and but is relatively expensive from other methods.
- Mobile applications: This method has changed the era of advertising. Use of applications is the easiest way to reach the customers. This method also allows the companies to update the customers about any modifications in the product.
P.3.3 Evaluate the suitability of different methods of distribution used to sell a holiday for different types of tour operator.
Any product information that has been generated needs to be distributed by one or the other way. Distribution is the process of movement of products from the producer to consumer. The distribution can be direct or indirect. Direct distribution methods allow direct contact of the producer and the consumer while indirect methods involve intermediaries to supply the product.
Two types of distribution channels
- Direct channel: The method involves direct selling of the product without any intermediary’s involvement. This method is flexible in nature as it involves greater control due to direct communication with the customers. The feedback can be received from the customers at the time of selling and promoting the products. (Clarke, 2010)
- Indirect channel: Indirect channel does not allow the direct contact between the supplier and the customer as it involves the mediators that support the sales. It is a costly method as it also considers the cost of the intermediaries.
Methods of distribution used by different operators:
- OTA’s (Online Travel Agencies): These agencies may or may not be physically present. They provide the customers with the list of the tour packages by different operators and allow them to click and book their trips online. It uses pay per click format. All the tour operators to enhance their sales and bookings should use this method. (Moore and Doherty, 2011)
- Government websites: Government websites provide the platform to the tour operators to communicate with the customers by posting their tour packages information on the site. Government sites are mainly for the local tour operators that deal with local and native tourists. It is the most effective platform to be used because government websites always found to be reliable by the customers.
- VIC’s (Visitors Information Centres): These centres allow the tour operators to drop off their flyers and leaflets along with their phone numbers. The customers can approach these centres and search out for the best tour package for themselves. They can get the contact number of the operators at the centres, so that they can contact the operators for further bookings and information.
- Daily deal websites: Daily deal sites provide the customers with the gift vouchers and other discounts on the tour packages offered by the operators. These sites can be best utilised at the time of slow business period to attract customers.
- Concierge services: Some of the hotels and motels provide these services. It is the service in which hotel and motels act as the intermediaries to attract the guests living in their hotels or visiting their place. All the local tour operators should drop off their leaflets with these hotels so that they can promote their packages to the potential customers. (Sigala, Christou and Gretzel, 2012).
Task 4
LO4 Understand strategic and tactical decision making for tour operators
P4.1 Evaluate the strategic decisions made by different types of tour operator.
Strategic decision-making is the ongoing process to achieve the goals and objectives of the organisation. It is very important for the organisation to bring out modifications in their processes and structure according to the current requirement and these changes need the management to make strategic decisions that provides the company with the long-term effects. In terms of tourism industry, many strategic decisions can be made considering different areas of business. Following are the some of the strategic decisions made by the tour operators: (Sigala, Christou and Gretzel, 2012).
- Pricing strategies: Price is the amount of money that has been paid by the customers in order to buy the products. Pricing of the product coveys about quality and quantity of the product. Tour operators need to make their pricing in such a way that somehow describes their product to the customers. The pricing strategies by the tour operators have been categorised into three broad areas:
- Premium pricing: This approach allows the operators to set the prices higher than the competitors to display the image of the product as premium.
- Value for money: Providing quality at the medium prices is the basic agenda of the operators who opt for this practice. (Cobb, 2003).
- Cheap value: This represents budget pricing by lowering the prices to expand the business or to enter into the industry. Thomson Cook uses the strategy of single pricing for its products. According to this strategy, price of the tour package should be same at all the mediums of distribution. This falls under the category of premium pricing by Thomas Cook.
- Surcharge policy: Surcharge pricing is the strategy is about raising the prices so high at the time of peak seasons. During the time of price rise of oil in UK, Thomas Cook travels reintroduced their bills by adding fuel surcharges.
- Image positioning or Branding: Brand identity provides a differentiated image to the product as well as to the company. Brand image of the company creates a loyalty among the customers towards the brand. P & O Cruises claims that 60% of their customers are loyal to the brand as they do repeated purchase from the company.
- Product choice: Product is what is actually delivered to the customer. In tourism industry, the tour packages are considered as product that needs to be sold in order to provide best travelling experiences to the tourists. Kuoni travels provide a wide range of destination products to the customers and are specialised in long haul resort holidays.
- Distribution channel: There are two types of distribution channels that have been used by the travel operators for supply of the products. Direct selling is one of the types that involve the direct communication of the operator with the tourists. Another type is the indirect channel that involves the intermediaries in between the supplier and the end users. Travel operators like TUI, Thomas Cook etc use both the channels as the method of distribution to reach their potential customers in masses.
P4.2 Compare the tactical decisions that could be taken by a selected tour operator in different situations.
Many decisions have to be taken by the management of the organisation to achieve the ultimate goals of the same. These decisions have been taken at different levels. These levels involve strategic, tactical and operational. Tactical level decisions are the medium- term decisions that deal with the implementation of the strategies. These decisions are taken by the head of the departments and generally affect a particular functional area. Below are the tactical decisions that need to be taken by the tour operators: (earth-net., 2013).
- Tactical responses
- Tactical pricing
- Tactical marketing
- Tactical planning
Tactical responses can be given to the internal as well as the external factors that act as the stimuli for the organisation. Different tour operators need to take decisions in response to the external and internal environment as well as according to the competitors. Change in the prices according to the change in the prices and economy of the country is another tactical decision that should be taken to survive in the market. Surcharge pricing by Thomas Cook at the time of price rise of oil is the most relevant example of tactical pricing. It considers seasonal planning, early bird pricing, fluid pricing etc. Fluid pricing is about selling a particular number of packages at cheap prices and then raise the prices with time. Tactical marketing involves the implementation of the marketing strategies by making decisions according to the market conditions. Many tour operators use internet as the medium to target their market because this era is more into online surfing rather than offline information gathering. The tour operators should conduct tactical planning. This planning involves decisions regarding how to implement the strategies to achieve the short-term objectives of the company.
Conclusion
Tour operators have been categorised according to the customers they serve and according to the type of products they provide. The four types of tour operators are inbound, outbound, tailor made and domestic. The tourism industry is developing with the development in the requirement of the people to travel for pleasure and entertainment. Tour operators play a very important role in providing travelling services to the customers. There are different trade bodies that interfere in the tourism industry with their part of providing funds and advice to the operators for their proper functioning. These organisations involve UK CAA, FTO, and AITO etc. Planning s the very important aspect that needs to be considered by the operators to manage the trips for the tourists. They need to make strategic and tactical decision according to the external and internal environmental situation of the industry and the market.
References
Books
- Cobb, V. (2003). The package tour industry. [Hertford]: M-Y Books Ltd.
- Moore, D. and Doherty, A. (2011). United States travel and tourism industry. Hauppauge, N.Y.: Nova Science Publisher's, Inc.
- Page, S. and Connell, J. (2010). Tourism. Los Angeles: SAGE.
- Sigala, M., Christou, E. and Gretzel, U. (2012). Social media in travel, tourism and hospitality. Farnham, Surrey, Burlington, VT: Ashgate Pub.
- Walker, R. and Harding, K. (2007). Tourism. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Journals:
- Clarke, A. (2010). Operations Management in the Travel Industry. Tourism Management, 31(6), pp.964-965.
- Goretti Sanches Lima, M. (2013). Package Travel, Package Holidays and Package Tours: Aspects of ‘package travel’ relating to travel and tourism contracts in the EU and Brazil. IFTTA Law Review, 3(2).
- Koenig-Lewis, N. and Bischoff, E. (2010). Developing Effective Strategies for Tackling Seasonality in the Tourism Industry. Tourism and Hospitality Planning & Development, 7(4), pp.395-413.
- Nikraftar, T. and Hosseini, E. (2016). Factors affecting entrepreneurial opportunities recognition in tourism small and medium sized enterprises. Tourism Review, 71(1), pp.6-17.
Websites
- earth-net. (2013). What is Responsible tourism?. [online] Available at: https://earth-net.eu/what-is-responsible-tourism/definition-of-the-concept/ [Accessed 14 Oct. 2016].
- Thomascook.com. (2016). Pricing Terms and Conditions on Offers | Thomas Cook. [online] Available at: https://www.thomascook.com/pricing-terms-conditions/ [Accessed 14 Oct. 2016].
- European Cities Marketing. (2015). European City tourism to resume positive growth in 2014, bolstered by international bednights and the recovery of traditional markets - European Cities Marketing. [online] Available at: http://www.europeancitiesmarketing.com/european-city-tourism-resume-positive-growth-2014-bolstered-international-bednights-recov [Accessed 14 Oct. 2016]
Details
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution