- support@locusassignments.com
Unit 2 Assignment on Marketing Mix Strategy

|
Program |
Diploma in Business (Marketing) |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 4 Marketing Principles |
|
QFC Level |
Level 5 |
Introduction
Marketing principles refers to different activities involve in transfer of goods and services from seller to customer. The activities like pricing, promotion, distribution etc. This term is also interlinked for achieving the objectives and competitive advantage to survive in dynamic environment. The report will provide the explanation about marketing process that is adopted by British SME for marketing and the factors influencing the marketing decision. Further it shows how distribution and pricing strategy helps in gaining the competitive advantage in market along with giving clear distinction about domestic and international market. In the other part, the report will provide explanation on segmentation, targeting and positioning criteria for Tesco and plan the marketing mix of two different segments in the current case. Tesco profits have grown in just 13 years by more than four and a half time and it is the largest retail supermarket stores and grocery department itself have 30.5 percent share that is incredible for the success of the Tesco.
TASK 1
1. Various elements of marketing process for British SME
Marketing is the wide platform to interact with consumer and to offer variety of their products and services. It is the process to achieve the desired goals and objectives with assigning right work to right employee at the right time and to provide the product at reasonable price to achieve the competitive advantages. The following are the key elements of marketing process which can be used by British SME:

- Customer delight- To attract more and more customer, British SME has to emphasis on the need of marketing programme which provides the benefits such as discount, promotions and gifts (Alam, 2016). This would help organisation for retention of client for longer period and builds image.
- Customised products- For achieving the British SME goals, the organisation has to make such marketing strategy that focus on consumer needs, their taste and preference and accordingly analysing and designing the products and services.
2. Marketing orientation and cost benefits
Marketing orientation is the process of providing product function and product efficiency along with customer needs and desires for delivering the product. If British SME will follow the marketing orientation they will get the benefits:
- Customer satisfaction- Through orientation, organisation will achieve the customer satisfaction that will maintain the efficiency of the business (Albuquerque.et.al. 2012). For achieving the benefits organisation needs to focus on quality and requirement of the customer.
- Long term profitability- With marketing orientation organisation like British SME gain the long term profits by providing quality products and services with the policy of retaining the customer for the longer time. The use of online services helps to establish the profits through adequately resolving the customer’s issues to retain them for longer period.
3. Macro and Micro environmental factors have influence on marketing decision

Figure 2 Macro and Micro factors affecting marketing decisions
Macro environment is broader in term and affects the larger part of the society. The factors affecting marketing decision in British SME are political, economical, social, technological, environmental and legal factor. The organisation needs to considered political scenario their rules and regulation of the government, economic fluctuation in the economy, social values are not affected by the marketing products, technological advancement is inbuilt in marketing strategy, the products are environmental friendly and make sure that organisation uses recycling process and legal formalities are essential for sustainability and development of product and to build the market reputation and customer satisfaction.
Micro environment is narrow in term and affects the internal environment of the organisation. The factors affecting marketing decision in British SME are supplier, competitor, distributor and public. According to British SME, SWOT is basically used to analyse the internal environment (Jobber and Ellis-Chadwick, 2012). Strength of the British SME business is providing good quality of their products and services, weaknesses in British SME is that less use of IT tools for decision making, opportunities can be to enter into the international market like India where they can achieve good profits and threats can be from competitors, economic fluctuations etc has a significant impact on marketing decision.
4. Difference in international marketing and domestic marketing
Table 1 International and Domestic Marketing
|
International Marketing |
Domestic Marketing |
|
Marketing over the geographical boundaries and involves production, distribution and promotion activities. |
Marketing within the geographical boundaries of the nation.
|
|
This marketing requires heavy investment |
Less investment and effective |
|
This marketing involves various barriers and risk. |
Involves less barrier and low risk |
|
Use of latest technology that involves licensing and marketing regulations |
Limited technology use that involves short licensing and understanding of marketing. |
|
Nature of the customer varies that requires knowledgeable human asset (Rezaei and Ortt, 2013). |
Nature of customer is almost same because it target on particular consumers. |
5. Development of products to sustain competitive advantage
To survive in competitive environment the British SME should know their core competencies to provide excellent product and services to their clients. Developing and analysing the plan is required to achieve the desired targets. Design and development of the product plays a critical role for attaining the competitive advantage. The core advantage of British SME is that it provides a wide range of quality products and organisation should focus on the competencies to retain the customer for the longer period of time. The organisation even should considered the purchasing power of the individual in the development phase only and manufacture the goods according to the customer willing to pay for the product with customer satisfaction (Rothaermel, 2015). This will help businesses to gain the competitive advantage by considering their needs.
In addition, British SME can use the segmentation and targeting strategy in development and research work and can provide additional benefits to attract the customer like reasonable price, quality assurance, promotions & gift and after sales services to gain the competitive advantage and for retention of customer for long period and to build image of the business. Though development and research is a lengthy process that involves important assets like time and cost of the human, but then to for gaining advantages from competitors it is beneficial and even essential for organisation to carry the work of development and in long run the cost is covered easily by retaining the customer and achieving the desired profits.
6. Distribution of products to provide customer conveniences
For distribution of the products and services is important and critical role of the organisation. For now many reputed organisation like British SME are moving toward the goal of providing goods to the customer on the desk of the customer by implementing technological tools for distribution of products with affordable pricing and customer satisfaction. The most common method is adopted i.e. online sales.

Figure 3: Image for Online Sale
In current scenario, the customer prefers the online buying of products and services and British SME has to focus on online marketing and sales, distribution of the product. This would be cost effective for the organisation in terms of human resource and infrastructure. The customer is benefited with availability of wide variety of different products and each and everything that is related to human being is available on online websites. Though there are other means also for the distribution of product to consumer i.e. through retail stores, departmental stores, intermediary or agents etc (Lemmens, 2015). A general chain is followed from manufacture to intermediary, agents or distributor and then to retail stores or shops and finally to end consumer. Normally this is lengthy chain in current scenario.
7. How prices reflects the objectives and market condition of organization
Every organisation tries to fix that price of the product from which the objectives and market conditions are fulfilled by them. Pricing strategy is normally based on the competitor’s price for the similar product. The main objective of the business is to survive in competitive environment and to attain the desired profits and growth and the price of the product would reflect the market condition by the demand and selling of the product. If the customer is giving the good response for the particular product and generating target profit then the market conditions are met.
Product launch in the market should be attractive and presentable because the young youth generally have a nature to use the new products introduce in the market, this is also market condition. Customer’s wishing to pay the price only when their purpose is solved for purchasing the product (Maniatis, 2015). For example, British SME now wishes to expand their business toward the international market, for that the organisation would set their prices by keeping the prices of the international competitor’s in mind and to achieve the desired objective.
8. Promotional activities to achieve the objectives
To achieve the objectives of the organisation the organisation needs to plan for promotional activities that help to achieve the goals of the business. For that British SME uses various promotional mix tools.
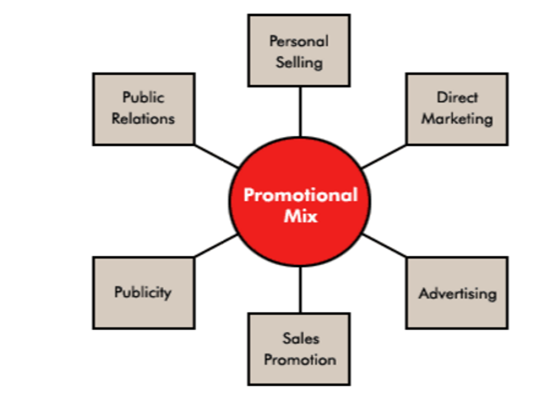
Figure 4 Promotional Activities
Promotional activities are personal selling which includes selling through door to door marketing of the product, direct marketing involves direct relation between manufacture and customer a very good example in direct marketing is online marketing activity where manufacture reaches the customer directly through a common platform, advertising can be done through television, newspaper, magazines and social websites which people visit often, sales promotion activities includes benefits associated with the sales i.e. good quality at normal price, discounts, coupons etc., publicity activity is same as advertising about the product, public relation activity can be done through closely relating the goods with the consumer needs and preferences and ignoring unfavourable publicity so that a relationship is developed between the organisation and customer (Viswanathan.et.al. 2014). British SME needs to target that promotional activity from the above that help to achieve the objectives and growth of the business.
9. Additional elements of marketing mix
Previously, there were four traditional marketing mix but now it has been extended to seven marketing mix.

Figure 5 Elements of Marketing mix
The additional element of marketing mix that affects the British SME:
- People: This is the important element of the marketing mix. Organisation need to give time and resource to this mix because if right work is not given to the right person at the right time then entire service would give a bad image to the entire service. By training and educating the staff the better service and communication would be possible.
- Process: The organisations need to have a standard process for marketing the product. The basic process should involve delivering the same services to every customer at any time. For that British SME should evaluate the new process for marketing like direct or personal marketing (Zerit.et.al. ).
- Physical evidence: This refers to organisation structure for delivering their services like retail outlets in malls or markets etc. This activity would be benefited to both customers as well as to British SME by having a platform for sell because comfort and personal satisfaction would be provided to the consumer.
Contact us
Get assignment help from full time dedicated experts of Locus assignments.
Call us: +44 – 7497 786 317
Email: support@locusassignments.com
TASK 2
1. Segmentation criteria that can be used by Tesco for products in different markets
Segmentation is a marketing concept that divides the complete market into smaller subsets comprising of consumers with a similar taste, demand and preference. Market segment is a small unit that comprises individuals who think on the same line and have similar interest. Tesco should use demographic segmentation for their products in different markets. Demographic segmentation is marketing segmentation that consists age, race, religion, gender, family size, ethnicity, income, and education. Demographic segmentation can be used into several markets to help an organization target its consumers more accurately. Through demographic segmentation Tesco can categorize the needs of consumers (Wedel and Kamakura, 2012). There are different basis of market segmentation that are based on gender, age group, income, occupation. One of the main advantages of demographic segmentation is that the information that is needed will be readily available for Tesco. For example, automobile industries can market their cars to different age groups, income levels, and genders.
- Segmentation in age: This marketing concept utilizes different marketing approaches for different age categories for population. The concept is based on the fact that consumer needs and desires change with age. According to the age and life-cycle segmentation, consumers’ age categories are divided into four segments: child, young adult, adult, and older adult. Some companies offer similar products in different versions according to the age and life-cycle segmentation. Segmentation in age will help Tesco to develop product according to age in society.
- Segmentation in income: Tesco should develop products according to section and class of society. Upper middle class section of society wants product in good quality and quantity. So the organization should develop product according to the class of income of the society. A low income section wants product in good quantity and can be managed with quality, according to that way product should be developed.
2. Main targeting strategies organizations use and suitable targeting strategy Tesco can adopt for a selected product.
For an organisation, targeting strategy is a strategy for identifying the potential customers to whom organization can sell its products/services to. There are various segments in any market.
There are four basic target marketing strategies.
- Customized targeting
- Undifferentiated targeting
- Focus or concentrated targeting
- Multi-segment targeting or differentiated marketing
3 Behaviour of buyers that affects marketing activities of Tesco in different buying situations
Consumer buying behaviour is the sum total of a consumer's attitudes, preferences, intentions, and decisions regarding the consumer's behaviour in the marketplace when purchasing a product or service. Personal behaviour of consumer plays a vital role in affecting market situation. The personal requirements of consumers are changing according to their need. If Tesco develops a product according to the personal requirement of a consumer then, they can be at dominating position in the modern and fast growing market. In personal requirement organization has to focus on age, occupation, lifestyle, personality and economic condition of consumer (Armstrong.et.al. 2014). These requirement changes time to time which should be noted by the organization like Tesco at regular intervals of time.
Social factors also affect the market activities of an organization: Every individual has some people around who influence him/her in any way. Reference groups comprise of people that individuals compare themselves with. Every individual knows some people in the society who become their idols in due course of time. Social factors can reference groups, relatives, family members. For example Tesco should target the festive season. In these season consumer generally purchase good quantity of goods. Through social factors organization can know about the patter of likes and dislikes of consumer.
4. New positioning for a selected product by Tesco
Product positioning is the process marketers use to determine how to best communicate their products' attributes to their target customers based on customer needs, competitive pressures, available communication channels and carefully crafted key messages. Data collection is one of the most important processes of positioning of product.
Effective positioning of product is important for succeeding to capture market; positioning becomes more important for a new product. For better positioning of new products, Tesco can use product life cycle software. Tesco can measure and track product's position directly and manually. Among the important element of marketing plan is the positioning of the product. It consists of customer needs and communication channels. For example, if Tesco launch’s an electronic product which is new in market. Then it should perform market research of that product, organization should create brand image with pricing strategy (Dunning, 2012).
Proper positioning of product helps customer identify the features of product for which they intend to buy the product. Once the customers are aware about the product features and specification, they can buy or recommend product to others.
Positioning of new product must focus on delivering distinctive features which are not common in the market. This would helps in attracting customers towards the market. Keeping all this in mind if Tesco can promote a new product in market and chances of becoming successful of that product will increase in market. Product should have sustainable advantage. Positioning of new product should not be static. It should change from time to time.
5. Planning marketing mixes for two different segments Tesco caters
Marketing Mix is defined as the activities which an organization needs to focus upon for positioning of its products. The components of marketing mix are Price, Product, Promotion and Place.
- Product: Tesco should develop product according to age of consumer. Different age group people have different likings and disliking. A youngster would prefer modern electronic gadgets as compared to old adult. Same is the case with income factor. Upper middle class people would prefer good standard products as compared to low income earning section.
- Price: Modern generation youngsters generally prefer offers and extra benefits on products. They easily get attracted towards new offers and incentives which are offered by organization as compared to adult people. This is not in case of adults, they purchase product at optimum rate. Pricing factor is most important in case of income earning section of society (Kotler,.et.al. 2015). High earning section of society would prefer luxury goods as compared to low earning income group.
- Place: Youngsters would prefer to purchase products online as they use gadgets a lot and they have knowledge of e-commerce. But this case is not with adult people; they like to purchase goods physically because adults are not sure about the quality of product online. A low income individual would like to purchase goods physically as compared to high income class people.
- Promotion: Promotion is generally similar in case of all age group and income group. This is because organization wants to reach their customers through any ways; it may be youngsters and old adults. And same is the case with high earning people and low income people (Solomon, 2014). Organization tries to cover each and every sector of society so that its sales volume increases.
6. Differences in marketing products and services to businesses in contrast to consumers
Table 2: Table 1: Difference between B2B and B2C marketing
|
Basis |
Business-to-business |
Business-to-Customer |
|
Focus |
Focus is on logic of product |
Focus on benefits of the product |
|
Distribution channel |
There is generally one distribution channel |
Customer can demand variety of distribution channels |
|
Market planning |
The substance of market planning should be detailed |
Market planning will include common need of consumers. |
|
Content |
High detailed content is required |
This is not in case of B2B |
|
Command chain |
B2B marketers have much longer chain of command |
In B2C an individual typically makes their own command chain (Medarac.et.al. 2016). |
Decision-makers, customer volume, type of buyers, sales cycle are some basis which differentiates between business to business and business to customers. In b2b communication channels are between two different organizations regarding; marketing of their products. In case of b2c communication channels is between business and their customers. In b2c business always focuses on modernization of product and keeps their eye on reviews made my customers. In b2b organization always try to focus on increasing their quantitative aspects as compared to b2c. Overall transaction of business to business is more as compared to business to customers.
Conclusion
From the above study, in British SME marketing principles and practices are considered for achieving the objectives of the business. Report includes process of marketing and identified the impact on decision making for marketing and development. Additionally it has discussed the various promotional activity, distribution and pricing method that affect the objectives and market conditions of the British SME. In the next part, report has undertaken the case study of Tesco and provided the brief discussion about segmentation, targeting and positioning of products. Further it gives a marketing mix for two different segments in Tesco by illustrating demographic and geographic. The report will also describe about difference in various market with respect to customer.
References
Alam, M., 2016. Financial effectiveness of sales promotional activities.
Albuquerque, P., Pavlidis, P., Chatow, U., Chen, K.Y. and Jamal, Z., 2012. Evaluating promotional activities in an online two-sided market of user-generated content. Marketing Science, 31(3), pp.406-432.
Clarke III, I., 2013. Handbook of Niche Marketing: Principles and Practice.Journal of Consumer Marketing .
Dunning, J.H., 2012. International Production and the Multinational Enterprise (RLE International Business). Routledge.
Jobber, D. and Ellis-Chadwick, F., 2012. Principles and practice of marketing (No. 7th). McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
Lemmens, G.H., 2015. Differences in framing activities between B2B and B2C contexts.
Maniatis, P., 2015. Investigating factors influencing consumer decision-making while choosing green products. Journal of Cleaner Production.
Rezaei, J. and Ortt, R., 2013. Multi-criteria supplier segmentation using a fuzzy preference relations based AHP. European Journal of Operational Research, 225(1), pp.75-84.
Rothaermel, F.T., 2015. Strategic management. McGraw-Hill.
Solomon, M.R., 2014. Consumer behavior: Buying, having, and being. Engelwood Cliffs, NJ: prentice Hall.
Viswanathan, M., Jung, K., Venugopal, S., Minefee, I. and Jung, I.W., 2014. Subsistence and sustainability from micro-level behavioral insights to macro-level implications on consumption, conservation, and the environment.Journal of Macromarketing, 34(1), pp.8-27.
Wedel, M. and Kamakura, W.A., 2012. Market segmentation: Conceptual and methodological foundations (Vol. 8). Springer Science & Business Media.
Zeriti, A., Robson, M.J., Spyropoulou, S. and Leonidou, C.N., 2014. Sustainable export marketing strategy fit and performance. Journal of International Marketing, 22(4), pp.44-66.
Need Help with Your Assignment?
Get expert guidance from top professionals & submit your work with confidence.
Fast • Reliable • Expert Support
Upload NowDetails
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution


