- support@locusassignments.com
Unit 2 Assignment on Managing Financial Resources - Radisson Plc

|
Program |
Diploma in Business |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 2 Managing Financial Resources - Radisson Plc |
|
QFC Level |
Level 5 |
Introduction
Radisson Plc is a medium sized enterprise which is indulged in the manufacturing of software and is based at London. The company recently acquired a contract to supply bespoke software for many companies in UK for long term. Bespoke software is a kind of software which is customized for the client in accordance with their needs and specifications for the software. Thus the operations manager of the company believes that the market share of company in the industry will increase since there are lot of opportunities for company to expand its operations. This unit 2 assignment on managing financial resources - Radisson Plc discusses the methods and procedures for managing the financial resources of the operations of business. The sources of finance for the operations of company and its expansion plan, their implications, cost of funding the project, importance of financial planning, recommended financing option, budgets and variance analysis, cost fvolume profit analysis, investment appraisal techniques, financial statements analysis, interpretation of financial ratios, comparison of company performance with peers etc are some elements of managing financial resources of a business which are included in this report for the expansion plan of Radisson Plc.

Task 1
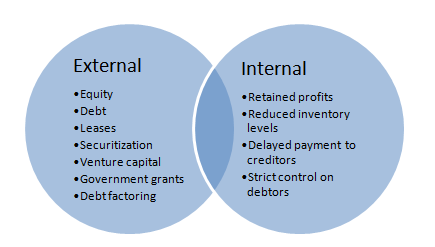
A. Sources of finance and their implications for the operations of business
The sources of finance available for the business of Radisson Plc and its operations which relate to the manufacturing of software as well as the implications of these sources are as follows:
- Equity financing – This type of financing involves rising of funds for the business from the owners of the business. The owners invest their capital in the business known as equity which is utilised for the purposes of business and earn returns in the form of dividends. It includes issue of equity and preference shares. This type of financing comprise of the cost of payment of dividends which are not tax efficient as compared to interest in debt financing.
- Debt financing – This type of source of finance is raising of funds in the form of loans or debts from external sources which includes bank overdraft, loans from financial institutions, issue of bonds, term loans and other borrowings. The cost involved in this source is the amount of interest. However, the interest payment has attached tax benefit also.
- Lease and hire purchase – In this source of finance the business instead of buying an asset agree to take on lease or hire purchase from a third party who buys such asset. Thus the huge amount needs not to be invested and also tax benefits can be availed in the form of tax saving on payment of lease rentals.
- Reduced inventory levels – The management of inventory and maintaining accurate inventory levels by the business saves the higher inventory costs for the business. Thus these sources of finance results in benefit of opportunity cost saving for the business in the form of saving of amount invested on inventories (Bernstein, 2015).
- Retained profits – This source of finance relates to generating the funds internally by retaining the profits of a business for long term rather than distributing them as dividends to the shareholders or owners of equity of business. There is no cost associated with this form of financing and the amount is also easily and quickly available. Also tax benefits can be availed from non-payment of tax on dividends. However this involves higher risks for the investors since more money is invested in the business.
- Government grants – It includes financial accounting assistance received by the business from the government in form of tax benefits, grants, subsidies, loan guarantee schemes, exemptions etc which are available only to some form of businesses belonging to specified business sector or industry. This form of financing also does not involve additional cost but is difficult to procure.
B. Evaluation of appropriate sources for expansion plan
The expansion plan for Radisson plc is to enter into contract with various companies in UK to supply the bespoke software. The appropriate sources of finance for this expansion plan for company are as follows:
- Debt financing - The company can procure loans from banks on the basis of contracts entered into with different companies as guarantee or security. This will involve interest cost to be payable on the bank loan. This type of finance source is risky but since the company has contracts with the companies to supply the software, therefore it can easily repay the loan after the expansion plan is implemented and the contracts are completed.
- Government grants – Since the company is a manufacturing entity indulged in the manufacturing of software and also belongs to the IT sector, therefore it will be easy for Radisson place to procure government assistance in the form of grants or tax benefits and tax exemptions from the profits of manufacturing operations.
- Lease – Since the company do not have high amounts of initial investment, thus it shall procure the assets of business on lease or hire purchase under monthly or yearly instalment payments rather than purchasing the assets itself. Since this will result in tax benefits for the business.
- Venture capital – Under this source of finance the venture capitalists provide funds for the expansion project or development project in relation to business at all the stages of the project from start-up to expansion and completion. These investors also monitor the performance of business operations. Thus it will be an appropriate source of finance for the expansion plan of company (Bhattacharya, 2014).
Contact us
Get assignment help from full time dedicated experts of Locus assignments.
Call us: +44 – 7497 786 317Email: support@locusassignments.com
Task 2
A. Analysis of cost of funding the project
Equity versus debt financing
|
|
Sources |
Cost implications |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Equity |
|
The cost associated with this source of finance is the payment of dividends annually from the earnings and tax implications from such payments. The opportunity cost is the cost of capital which is minimum required rate of return (Caglayan, 2014). |
There are lesser risks associated with this form of financing since the payment of dividend has to be made out of retained earnings after deduction of all the costs of business. |
Higher cost and no tax relief or tax benefits to the business are the disadvantages of this form of funding. |
|
Debt |
|
The cost associated with this source of finance is the payment of interest to the providers of loans However tax benefits are available on payment of interest on loans. Opportunity cost is the required rate of return. |
The advantage in this source of funding is lesser cost due to benefits of tax saving on interest payment. Any amount can be procured for the investment in the projects without limit. |
The disadvantages include regular payments to be made at periodical intervals, even in case of losses suffered by business. Huge burden of debt increase the levels of financial and liquidity risk of business. |
Recommendation – On the basis of analysis of cost of equity and debt funding for the project, the company is recommended to adopt debt financing for the expansion plan since after completion of contracts for supply of software, the company will be easily able to repay the loans and thus reduce the risks. Also the company can avail tax benefits on interest payment.
B. Importance of financial planning and Information needs for financial decisions making
Importance of financial planning: Financial planning refers to as the process of forecasting the financial results of a specific project or business determining the manner in which the financial resources of a business or a company can be used in the best possible manner. Financial planning is done with the objective of achieving long-term and short term goals of a business. There are many benefits of financial planning which justify the importance of financial planning for a business. They are as follows:
- The forecasts help in determining the cash inflow and cash outflow of a period in advance.
- It helps in indentifying the accurate time and method of raising the funds for the operations of business to ensure optimum use of financial resources.
- It helps in cost reduction and cost control by comparing the financial plan with the actual costs and benefits.
- It facilitates appropriate pricing of the products and services of business.
- Through the forecasting of profits the probability of achieving the objectives of organization can be easily determined.
Information needs for financial decision making: Financial decision making is the process of assessing the financial viability of a project or business operations on the basis of financial information of that business or project. Thus information is the most important element of the financial decision making process. Information from all the levels of management including strategic, operational and tactical is needed for the appropriate decision making. Financial decision making involves mainly quantitative information as compared to the qualitative information which is required for some specific areas such as opportunity cost. Thus all the accounting information related to the business and its different departments and functions is relevant for the purpose of financial decision making (Serrasquerio, 2011).
C. Impact of suggested financing option on financial statement
The suggested financing option for the expansion plan of company is debt financing which involves procurement of long-term loan from the bank. The impact of this option on the financial statements of Radisson Plc will be decrease in profits due to increase in interest cost as part of statement of profit and loss. Apart from this the non-current liabilities will increase in the Balance sheet on the asset side and the amount representing cash at bank will also increase at liabilities side. The cash flow statement will include cash inflow from financing activity as loan procurement. It will be recorded as follows:
Statement of financial position
|
|
£ million |
|
Assets |
|
|
Non-current Assets |
|
|
Cash at Bank |
100 |
|
Liabilities |
|
|
Non-current liabilities |
|
|
Bank loan |
100 |
Statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income
|
|
£ million |
|
Profit from operations |
64 |
|
Less: Interest paid |
8 |
|
Profit before tax |
56 |
|
Less: tax |
16.8 |
|
Profit after tax |
39.2 |
|
Dividend |
9.2 |
|
Retained Earnings |
30 |
Task 3
A. Importance of budget for variation
Budget is a kind of presentation of a plan of management in relation to its financial activities and financial performance in quantitative form for a specific period. A financial budget relates to the presentation of expectation of the management in terms of profits, financial position and cash flows from business activities for a specific period. Budget is used as an important tool for the monitoring of the actual performance from the standard performance expected from the business. The actual performance can be compared in context of all departments and sections and for all periods. This difference between actual and budget is known as variance. When actual performance is better it is favourable variance and vice versa. Thus for the monitoring and control of financial performance of Radisson Plc and make appropriate decisions with regards to cost control and achievement of long term and short term goals, the budget and variance analysis is very important (Yahya, 2012).
B. Calculation of unit cost and pricing decisions
Unit cost is the cost of each unit or product of the company’s business. It is calculated by adding the total costs of the company and dividing it by the number of units produced. The calculation of unit cost for the expansion plan of Radisson plc will be calculated by adding the total budgeted costs of the project which includes manufacturing of bespoke software for different companies individually and then dividing the total cost by the number of softwares supplied to that specific company. For example if total cost of supplying software to Logics software is £8 million and the number of softwares supplied to this company is 800, then the cost per unit will be £8,000,000/800 = £80,000 per software package. This method will be appropriate since the total cost of software will be different for each company in UK as these softwares will be customised.
C. Assessing viability using Investment appraisal techniques
Investment means any expenditure of capital nature which is done with the expectation of earning future economic benefits for many years. It involves a huge amount of money in the form of initial investment. Investment appraisal is an approach or a method which is used to select the best investment option or investment project. It involves origination of alternatives, screening of project options, and analysis of available alternatives, selection of feasible option and monitoring and review of the selected project option. Investment appraisal techniques are of two types discounting and non-discounting. Non-discounting techniques include Payback period analysis and Accounting Rate of Return (ARR), whereas discounting techniques include Net Present value (NPV) and Internal rate of Return (IRR).
Net Present Value – It is the investment appraisal technique which is used to assess the financial feasibility pouf an investment proposal in terms of cash flows. The net present value is the excess of present value of cash inflows from the project over present value of cash outflows invested in the project (Robison, 2015). It is the net benefit which is achieved from the project during the life of the project. If a project has a positive NPV it is worth accepting otherwise not. Also out of two mutually exclusive projects, the project with higher NPV shall be selected. The viability of expansion plan of Radisson Plc can be assessed by calculating NPV from the project as follows:
|
Cost of capital |
10% |
|
Life of project |
20 years |
|
Initial Investment |
£100 million |
|
Yearly cash inflow |
£20 million |
|
Present value of cash outflow |
£100 million |
|
Present value of cash inflow |
£122.8 million |
|
Net Present Value |
£22.8 million |
From the above calculation of NPV, it can be observed that the NPV from the project is positive and therefore the company shall undertake the project since the project has the potential to generate good returns for the company in the form of cash inflows during 10 years (Weber, 2014).
Task 4
A. Financial statements of Radisson Plc-
In every organisation there are required to maintain various financial statements which help in analysing and evaluating the various aspects related to the financial positioning of the company. The following are some financial statements of the company Radisson Plc.
Income statement: Income statement is a financial statement which shows the position of the organisation’s income and expenses and defines financial performance of the company for a defined accounting time period and also provides a base for taking effective decisions in organisation. Following is the income statement of the company.
|
Particular |
Amount (in Pound) |
|
Revenue |
120000 |
|
Cost of Goods sold |
65000 |
|
Gross Profit |
55000 |
|
Other income |
17000 |
|
Distribution Cost |
10000 |
|
Administration Expenses |
18000 |
|
Other Expenses |
3000 |
|
Finance charges |
1000 |
|
|
15000 |
|
Profit before tax |
40000 |
|
Income Tax |
12000 |
|
Net Profit |
28000 |
Statement of cash flow: This financial statement leads to track all the cash transactions in the company resulted from operating, investing and financial activities in the company for a specific time period and also defines the cash equivalents in the company. Following is the statement of cash flow of the company.
|
Particular |
Amount |
|
Cash flow from operating activities |
|
|
Operating Income (EBIT) |
48900 |
|
Depreciation expense |
11240 |
|
Loss in sale of expense |
730 |
|
Increase in Accounts Receivable |
-8466 |
|
Decrease in Accounts Payable |
-9737 |
|
Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities |
42667 |
|
Cash Flows from Investing Activities |
|
|
Sale of Equipment |
8900 |
|
Purchase of Equipment |
-10000 |
|
Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities |
1100 |
|
Cash Flows from Financing Activities |
|
|
Payment of Dividends |
-9000 |
|
Payment of Bond Payable |
-2000 |
|
Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities |
-11000 |
|
Net Change in Cash |
32767 |
|
Beginning Cash Balance |
11580 |
|
Ending Cash Balance |
31973 |
|
|
12374 |
Statement of financial position: This financial statement defines various assets and liabilities of the company which shows the actual position and solvency of the company in different aspects. Following is the balance sheet of the company (Puri, 2014).
|
Assets |
Amount |
|
|
|
|
Inventory |
31000 |
|
Supplies |
3800 |
|
Prepaid insurance |
1500 |
|
Investments |
36000 |
|
Plant and equipment |
33700 |
|
Goodwill |
10500 |
|
Total assets |
116500 |
|
|
|
|
Liabilities |
|
|
Accounts payable |
35900 |
|
Intereastpayble |
2900 |
|
Equity capital |
68900 |
|
Unearned revenue |
8800 |
|
Total Liabilities |
116500 |
B. Comparison of formats financial statements of two different companies
Financial statements of two different companies may be different as per the applicable financial reporting framework and accounting framework regulation applicable on such company. Other reasons for the differences include size of organization, type of organization, whether listed or not etc. The two companies for comparison of format of financial statements are Radisson plc which is a medium sized manufacturing company which is not publically traded or listed and other company is Merlin Entertainments Plc which is a listed company and belongs to service sector. The comparison of formats of financial statements of these two companies is as follows:
- Income Statement – The revenues of public company are higher than that of Radisson plc. Also the expenses are more in number and amount. The expenses of Radisson Plc include manufacturing expenses whereas Merlin Entertainments include more of selling and administrative expenses since it is a service company.
- Statement of financial position – The financial statements of manufacturing company include more tangible assets than that of service providing company. Another difference is that the listed company has share capital whereas the non listed company has only invested capital of owners of business.
- Statement of cash flows – These financial statements of both the companies involve more transactions from operational activities (Alin, 2014). however the cash flow statement of listed company include issue of equity shares as financing activity which is not included in the cash flow statement of Radisson Plc.
C. Interpretation of financial statements using ratios
The public limited company is Merlin Entertainments Plc and the other company is Radisson Plc. The comparison of financial ratios of the two companies is as follows:
Financial ratios of two companies
|
Ratios |
Radisson plc |
Merlin Entertainments Plc |
|
Profitability Ratio |
|
|
|
Profit Marguin Ratio (%) |
23.33 |
10.05 |
|
Return on Equity (%) |
40.63 |
24.29 |
|
Liquidity Ratio |
|
|
|
Current Ratio (%) |
0.7626 |
0.2786 |
|
Acid Test Ratio |
|
0.2317 |
|
Efficiency Ratio |
|
|
|
Inventory Turnover Ratio |
2.09 |
8.74 |
|
Asset Turnover Ratio |
1.03 |
1.46 |
Conclusion
From the above discussion about the techniques of managing financial resources and making appropriate decisions for a software manufacturing company and its expansion plan, it can be concluded that the financial investment decisions can be taken in an appropriate manner and efficient way through application of appropriate financial management operation and methods. From the evaluation of investment decision of Radisson Plc to expand its operations by entering into contracts to supply bespoke software to different companies in UK, it can be concluded that the project is feasible for the company and therefore it shall invest in the project through debt financing as recommended.
References
Ahmed, A.D., Dr & Bruce, K., Mr 2014;2016;, Conceptions of Professionalism: Meaningful Standards in Financial Planning, New edn, Gower, Farnham.
Ahmed, H. & Ak Md Hasnol Alwee Pg Md Salleh 2016, "Inclusive Islamic financial planning: a conceptual framework", International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 170.
Alin-Eliodor, T. 2014, "Financial Statements Analysis", Journal of Knowledge Management,vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 62-73.
Bernstein, A. 2015, "Show me the money: finding alternative sources of finance", Nursing And Residential Care, vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 398-401.
Bhattacharya, S. & Londhe, B.R. 2014, "Micro Entrepreneurship: Sources of Finance & Related Constraints", Procedia Economics and Finance, vol. 11, pp. 775-783.
Caglayan, M. & Demir, F. 2014, "Firm Productivity, Exchange Rate Movements, Sources of Finance, and Export Orientation", World Development, vol. 54, pp. 204-219.
Puri, A.K. 2014, "Financial Statement Analysis and Security Valuation", Abhigyan, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 74.
Robison, L.J., Barry, P.J. & Myers, R.J. 2015, "Consistent IRR and NPV rankings", Agricultural Finance Review, vol. 75, no. 4, pp. 499-513.
Serrasqueiro, Z., Maçãs Nunes, P. & Leitão, J. 2011, "Sources of finance for R&D investment: Empirical evidence from Portuguese SMEs using dynamic estimators", Innovation, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 187-206.
Need Help with Your Assignment?
Get expert guidance from top professionals & submit your work with confidence.
Fast • Reliable • Expert Support
Upload NowDetails
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution