- support@locusassignments.com
Unit 2 Managing Financial Resources Decisions Assignment - Sweet Menu

|
Program |
Diploma in Business |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 2 Managing Financial Resources Decisions - Sweet Menu |
|
QFC Level |
Level 5 |
Introduction
Finance or Financial resource is the prime requirement of the business. With the use of finance business perform various activities such as start a new business, expand the existing business, running routinely activities and many more. To get finance in market there are different sources are present that will be discussed in below unit 2 managing financial resources decisions assignment Sweet Menu. Raising funds is not sufficient enough it requires optimum utilisation and effective management of the funds. For this purpose there are different methods are available that will be discussed in below report. To make investment in different projects or investments company needs to evaluate their profitability and with this effect investment appraisal techniques will discussed and utilised in below report. Financial ratio analysis will be utilised for making effective comparison among two different companies of same industry such as Sweet menu restaurant and Blue Island restaurant.

Task 1
1.1 Identify the sources of finance available to a business.
The different sources of finance available to the Sweet menu for their business environment expansion plan get discussed below such as:
|
External Sources |
Finance get arranged other than business and owner is known as external sources. Below are some sources get discussed such as: |
|
Sources |
Description |
|
Bank loan |
Sweet menu contact the bank in order to get the funds against the securities. Bank lend the money and charge interest at adequate rate. This create long term liability over them. |
|
Bank overdraft |
Bank provide the facility of overdraft to Sweet menu according to which they are able to sign the cheque even they don't have sufficient funds in their bank account. Bank charge high rate of interest over this amount. |
|
Equity capital |
Sweet menu issue shares in order to get the funds to support their business expansion plan. They make issue of ordinary shares to do so. |
|
Leasing |
Sweet menu requires some new machinery or equipments to support expansion and for this purpose they took the required equipment on lease that helps in saving their available finance. They pay rentals against the use of lease equipment. |
|
Hire purchase |
Sweet menu requires some new machinery or equipments to support expansion and for this purpose they took the required equipment by availing hire purchase option and it helps in saving their available finance. They make payment of remaining amount in small instalments. Instalment include interest amount plus part of principle amount. |
|
Government grants |
Sweet menu took the government grants as they are small scale business. |
|
Internal Sources |
When finance get arranged within the business organisation get termed as internal sources. Below some sources get discussed such as: |
|
Sources |
Description |
|
Retained profits |
It is such funds that get made with the help of profit share. Every year Sweet menu took some part from their profits and put into reserve funds. This fund is utilised at the time of business expansion. |
|
Sale of fixed assets |
Sweet menu evaluate their assets and sold out such assets that are of no use or outdated. By selling these assets they effectively raise adequate funds to support their expansion plan. |
1.2 Assess the implications of the sources of finance identified in task 1.1
There are adequate level of implications are associated with the identified sources of finance such as:
|
Sources |
Legal |
Dilution |
Risk |
Finance |
|
Bank loan |
Legal contract is signed by Sweet menu and bank. |
No new owner is introduced. Bank get the interest over loan amount so they didn't get share in ownership. |
Failure of loan repayment results in to bankruptcy. Instalment must paid on regular basis. |
Huge cash get raised with it. During liquidation they get preference over unsecured loans. |
|
Bank overdraft |
Sweet menu and bank sign legal contract |
No new owner is introduced. Bank get the interest over overdraft amount so they didn't get share in ownership. |
Failure of overdraft repayment results in to bankruptcy. It must repaid on specified time. |
Required amount get raised. During liquidation they didn't get preference over secured loans. |
|
Equity capital |
Sweet menu get the approval from registrar to make issue of shares. |
Shareholders become owners. Issue of shares results into control dilution. |
Amount raised with the issue of shares didn't get repaid till liquidation. |
Dividend is paid out of profit share. During liquidation they get funds in the end of process. |
|
Leasing |
Sweet menu and lessor sign legal agreement to start lease. Lease agreement include all terms and conditions. |
Lessor get the rentals on regular basis. Lease didn't create additional owner for them. |
There is no risk as at the time of payment failure lessor is eligible to take back their assets. |
Small rentals need to be paid. During liquidation they get their remaining rentals and assets. |
|
Hire purchase |
Sweet menu and seller sign legal contract. Contract include all terms and conditions. |
Seller get the instalment on regular basis. Seller didn't become the owner of the company so control remain with Sweet menu only. |
Seller is eligible to take back the asset if Sweet menu fail to pay the instalment amount. |
Small amount instalments need to be paid. During liquidation they get their remaining instalment amount. |
|
Government grants |
Sweet menu need to fulfil the criteria. |
Government support their business and didn't become the owner. |
There is no risk is associated with it. |
The amount of grant didn't need to repay. |
|
Retained profits |
It is the own funds of the Sweet menu. |
There is no additional owner of the business organisation. |
There is no cost is associated so there is no risk. |
It lower down the share of profits that is given to the shareholders in the form of dividends. |
|
Sale of fixed assets |
Sale agreement signed among buyer and Sweet menu. |
Buyer become owner of the asset not of the business. So Sweet menu is attaining their ownership with them. |
There is no risk is involved unless they didn't sold useful asset as it impact their production capacity. |
Adequate level of funds get raised with the help of it. |
1.3 Evaluate the most appropriate sources of finance for Sweet Menu Restaurant expansion plans.
The most appropriate sources of finance are discussed below such as:
|
Sources |
Description |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Bank loan |
Sweet menu borrow funds from ban. They get agreed over the interest rate and time period of repayment. |
|
|
|
Equity shares |
Sweet menu issue ordinary shares in order to maintain capital gearing ratio. |
|
|
|
Retained profits |
Sweet menu utilise their reserve funds. |
|
|
Contact us
Get assignment help from full time dedicated experts of locus assignments.
Call us: +44 – 7497 786 317Email: support@locusassignments.com
Task 2
2.1 Analyse the costs of the different sources of finance that you have identified for Sweet Menu Restaurant in task 1.3 above.
The costs of different sources of finance get discussed below such as:
- Cost of debt: - The cost that paid over debt capital is termed as cost of debt. It make inclusion of interest amount that paid over loan amount. Sweet menu borrow funds from bank at agreed rate of interest. Borrowing funds are debt capital and interest paid is the cost associated with it (Barth, et. al., 2013).
- Cost of equity: - The cost that paid over the equity capital is termed as cost of equity. There are various cost paid in the form of administration fees, listing fees, issuance fees and more at the time of issuance of shares. After that dividend paid to the shareholders also considered as the cost of equity.
- Opportunity cost: - Retained profits having this cost associated with them as funds of retained profits get utilised for various purposes. Sweet menu evaluate the optimum utilisation of the retained profits and make use of them accordingly. There is no other cost is associated with it (Blanco, et. al., 2015).
2.2 Explain the importance of financial planning for Sweet Menu Restaurant with reference to the new business project.
Financial planning: It is an process of analysing the financing and investment options. It helps in projecting consequences in near future with the effect of current decision making. It get utilised for measuring performance in order to attain the set goals and decide alternatives to perform the tasks (Bird, et. al., 2014).
The importance of financial planning get discussed below such as:
- It get utilised for managing available income in efficient manner
- It results into increase in cash flows and also put adequate level of control over their spending or expenses.
- It helps in preparing strong capital base and also forecast strong financial future.
- It make identification of beneficial investment opportunities
- It helps in dealing with the emergency situation
- It helps in setting financial priorities
- It makes effective reduction in the uncertainties.
- It make effective allocation of the available funds to meet their expenses (Bird, et. al., 2014).
Steps involved in the process of financial planning such as:
- Projection of managing financial statement
- Determining the requirement of funds
- Forecast related to the available funds
- Establish control system
- "Feedback loop": - A process of adjusting basic plan
- Performance based management compensation system (Croy, et. al., 2010).
2.3 Assess the information needs of different decision makers in Sweet Menu Restaurant.
There are three types of decisions are there such as:
- Strategic decisions: Undertaken by top level management, long term and externally focused.
- Tactical decisions: Undertaken by middle level management, short term, internally focused and more detailed (Alin-Eliodor, 2014).
- Operational decisions: Undertaken by lower level management, daily basis decisions, focused internally and put direct impact over customers (Alin-Eliodor, 2014).
Different stakeholders requires different information such as: -
- Shareholders: They are the internal stakeholder as they are interested in profitability of the organisation. They evaluate the profitability information as they are getting dividend or not. They evaluate the factors such as availability of liquid funds for their future expansion plan.
- Management: They are interested in all type of information such as liquidity, profitability, financial position and others as they utilise it for making strategic decisions, policies and controlling measures for the betterment of business organisation (Puri, 2014).
- Employees: They are internal stakeholders and their interest is associated with their salaries and other benefits such as appraisals, bonuses and growth opportunities. They are interested in profitability information and their future expansion plan as they make decisions whether they stay with organisation in order to grow with them or not.
- Customers: They are external stakeholders and their interest is associated with profitability and quality information. They are the one who make consumption of their goods and services. They also evaluate the ethical compliance information in order to deal with them (Puri, 2014).
- Suppliers: They are external stakeholders and their interest is associated with profitability and liquidity as they evaluate the time period in which they get their funds. While supplying them they evaluate the liquidity capability in order to measure their capacity whether they get their funds timely or not.
- Government: They are external stakeholders and their interest is related to their profitability in order to assess the payable tax amount. They also evaluate their compliance whether they are processing their activities according to the set standards or not (Puri, 2014).
2.4 Using the most recent financial statement of Sweet Menu Restaurant given below, explain the impact of the sources of finance identified in task 1.3 on the financial statements of Sweet Menu Restaurant.
The flow of funds whether it is inflow or outflow put adequate level of impact over financial statements such as:
|
Sources of finance |
Balance sheet |
Profit and loss account |
Cash flow statement |
|
Bank loan |
It increases the cash balance under assets and increase long term liability with a head of bank loan. |
Fixed rate interest is paid over loan amount increases expenditure. It recorded under payments and reduces profit. |
It increases the inflow of cash under financing activities. Payment of interest lowers the cash balance. |
|
Bank overdraft |
It increases the cash balance under assets and increase short term liability with a head of bank overdraft. |
Fixed rate interest is paid over overdraft amount increases expenditure. It recorded under payments and reduces profit. |
It increases the inflow of cash under financing activities. Payment of interest lowers the cash balance. |
|
Equity capital |
It increases the cash balance under assets and increases the balance of equity capital under liabilities. |
Dividend is shared with the shareholders and it recorded under expenses. It lower down the profit share. |
It increases the cash balance of the financing activates with the issue of shares. Dividend payment reduces the cash balance. |
|
Leasing |
It increases the fixed assets balance and create a long term liability with the head of lease. |
Payment of rentals termed as expenses and recorded under expenditure. It lower down the profit. |
It decreases the investing cash balance due to the payment of rentals. |
|
Hire purchase |
It increases the fixed assets balance and create a short term liability with the head of hire purchases. |
Payment of instalments termed as expenses and recorded under expenditure. It lower down the profit. |
It decreases the investing cash balance due to the payment of rentals. |
|
Government grants |
It increases the cash balance under assets. |
There is no cost is associated so there is no impact over this statement. |
There is increase in the financing activities cash balance. |
|
Retained profits |
Putting amount in reserve funds increase in the cash balance under assets and also increase the reserve funds under equity capital. |
There is no cost is associated so there is no impact over this statement. |
It increases the operational activities cash balance. |
|
Sale of fixed assets |
It decreases the balance of fixed assets but with the same amount it increases the cash balance if it get sold for no profit-no loss. |
Profit over sales increases the revenues and total profit share and vice-versa. |
Sale of asset at par increases the cash balance of investing activities. |
Task 3
3.1 Analyse the budgets and make appropriate decisions
Budget: It is an financial and quantitative statement that get prepared for a defined time period and it showcase the planning for attaining the set objectives.
Features of budget:
- It helps in making accurate forecasting
- It is based on the organisation goals
- Information utilised is timely and accurate
- It get prepared with multilevel input
- In budget regular reviews are built in (Roper & Ruckes, 2012).
Problems associated with budgeting:
- The preparation process is too long
- Prepared budget didn't get changed even business decisions get changed
- In charge authority of budget are accountable in such areas even they have no responsibility (Roper & Ruckes, 2012)
Use of budget:
- It provide controlling power
- Utilised for forecasting
- It helps in setting priorities and organising needs.
- It helps in making adequate use of available funds (Roper & Ruckes, 2012)
Below is the cash budget prepared such as:
- Analysis: By analysing the above prepared budget it is observed that there is increase is both elements such as receipts and payments. The rate of increase of receipts is slow and inconsistent whereas the payments get increasing on constant speed. This gap results into negative cash balances at the end of the month. By evaluating the reason it is observed that Blue Island purchase the capital nature equipment by making cash payments that results into deficit of cash balance. Otherwise they are getting adequate receipts through which they meet out their payments easily (Gervais, et. al., 2011).
- Suggestion: After analysing the prepared budget it is suggested that Blue Island need not to make cash payments against capital expenditure as it lower down their cash availability. For making purchase of these capital equipments they need to evaluate other options such as bank loan or leasing or hire purchase. These options render adequate level of support in getting capital nature equipments. Bank loan and hire purchase charge interest and it results in tax relaxation benefit. So it is beneficial for them to utilise such options to make payment of their capital equipment (Gervais, et. al., 2011).
3.2 Explain the calculation of the unit costs (meal cost) and make pricing decisions using relevant information given above.
- Unit cost: The cost that get incurred while producing the one unit in the form of labour cost, material cost and many more.
- Methods of unit cost calculation: There are two methods get discussed below to calculate the unit cost in effective manner such as:
- Marginal costing: This costing method didn't include the fixed cost or indirect cost while calculating the unit cost. This method include only variable cost for the calculation of unit cost (Adkins & Paxson, 2014).
- Absorption costing: This costing method include variable as well as fixed cost (direct and indirect cost) for the calculation of the unit cost.
Unit cost calculation by following absorption costing such as:
Pricing decision: In the above table unit cost and price of meal both are calculated. For calculating unit cost absorption costing method is utilised in which all available cost get included to calculate unit cost (Adkins & Paxson, 2014). For pricing decision management utilise the cost-plus pricing method as according to this method they add mark up amount and VAT amount over the calculated unit cost. With the use of this method they become much capable in order to fix certain amount of profit for getting adequate profit margin (Adkins & Paxson, 2014).
3.3 Assess the viability of the two projects using investment appraisal techniques as follows;
a) Payback method and net present value (NPV) method for the two projects and identify which project should be approved by Blue Island Restaurant and explain why.
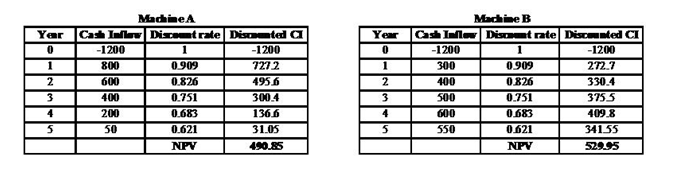
Net present value: The difference amount between the discounted inflow of cash and the investment made is termed as net present value. This difference amount is utilised for evaluating the profits associated with the investment. High positive difference amount shows high profitability and vice-versa.
Calculation:
[Note: In machine B calculation in the 5th year 50 is added into cash inflow of 500 as it is an residual value of the machine B]
- Decision: The above calculated NPV's of both machines shows that Machine B is attaining high positive difference amount that means it is more profitable as compare to the Machine A.
- Pay-back period: The time period in which the invested amount get recovered in the form of revenues and it get termed as pay-back period. It shows the risk level associated with investment. Lower time period shows that investment is having low risk and vice-versa (Saxena, 2015).
Calculations:
|
Machine A Payback period calculation |
|
1 year + {(£1,200 - £800) / £600} |
|
1 year + {£400/£600} |
|
1 year + 0.67 |
|
1.67 years or 1 year and 8 months |
|
Machine B Payback period calculation |
|
3 years + {(£1,200 - £1,200) / £500} |
|
3 years + {0/£500} |
|
3 year + 0 |
|
3 years |
- Decision: As per the calculation results it is observed that Machine A is less risky as compare to the Machine B because Machine A took 1 year and 8 months to recover their investment amount on the other hand Machine B took 3 years to do the same.
- Analysis: In the end of the discussion and results evaluation it is concluded that Machine B must be opted as it yields high profits as compare to the Machine A. Even Machine B is highly risk but then also it is adopted because high risk results into high profits (Baker & English, 2013).
Task 4
4.1 Discuss the main financial statements
- Financial statements: Those statements that get prepared by the management in order to record their different transactions so that after some time they make analysis over them and extract the useful information. The extracted information make inclusion of their profitability, liquidity, financial position and many more. This information is further utilised for making decision and framing policies. Below are the main financial statements get discussed such as:
- Profit and loss account: Management identify the transactions related to the income and the expenditure and make them record under this statement. This statement having two parts one is revenues or receipts and another one is expenditure or payments. First revenues or receipts get recorded and then payments or expenditure get recorded. When all the transactions get recorded then it is utilised for evaluating profits or loss for that period. This financial statement is utilised for profitability evaluation (Riedl & Srinivasan, 2010).
- Receipts: All the income received by the business in the form of sales revenue, interest received and any other income get recorded and termed as receipts.
- Payments: All the transactions shows payment by the business in the form of purchases, rent, salaries and wages and many more get recorded and termed as payments (Riedl & Srinivasan, 2010).
- Cash flow statement: Management identify the transactions related to the use of the cash and cash equivalent whether it is cash payment or cash receive get recorded under this statement. This statement having three sections and each sections has its own speciality as per which they record their transactions. All three sections are introduced for the purpose of rendering detailed information about the use of the cash and cash equivalent. This financial statement is utilised for liquidity evaluation
- Operating activities: Cash and cash equivalent utilised in operational activities get recorded under it such as salaries and wages paid in cash, administration expenses paid in cash and many more (Bradshaw, et. al., 2010).
- Investing activities: Cash and cash equivalent utilised in investing activities get recorded under it such as purchase of equipment, sale of fixed assets, loss on sale of fixed assets and many more.
- Financing activities: Cash and cash equivalent utilised in financing activities get recorded under it such as bank loan, interest paid on bank loan, issue of shares and many more.
- Balance sheet: Management prepare this statement to provide a summarised overview of their financial position. It helps in evaluating the financial position as it get segregated into three parts such as assets, liabilities and equity capital (Bradshaw, et. al., 2010). There is equation that helps in identifying whether the prepared statement is correct or not such as: -
Assets = Liabilities + Equity capital
Assets: It is anything that owned or leased by the organisation
Liabilities: these are such elements that claim against their assets in the form of creditor
Equity capital: it is the balance of all claims such as proprietor, shareholders against the firm's assets (Bradshaw, et. al., 2010).
4.2 Compare appropriate formats of financial statements for different types of business
There are three different type of business organisation are there such as sole trader, partnership and limited liability company and all these having different interest according to the interest of the their stakeholders. They prepare financial statements in order to satisfy the need of their stakeholders. Sole trader's financial statement are very simple and mainly serve to the owner's interest (Moehrle, et. al., 2010).
Comparison between Sole Trader and Limited company
- Sole trader's financial statements are not very complex in comparison to the limited company
- Sole trader's are not required to follow the standard of IFRS & GAAP while preparing their financial statements.
- In UK for sole traders it is not mandate to prepare balance sheet and income statement.
- All the capital expenditure items need to be recorded by the sole traders so that they maintain a proper record in order to claim capital allowances each tax year.
- Limited companies need to prepare financial statements such as balance sheet, income statement, cash flow and statement of owner's equity by following the set standards of the IFRS and GAAP (Moehrle, et. al., 2010).
Comparison between Sole Trader and Partnerships
- If sole trader is VAT registered then they need to maintain more detailed financial records.
- Normal audit need to be conducted in order to verify the transactions and helps in supporting the VAT return.
- In Partnership firms, financial statements get prepared in order to evaluate the profit and loss for the time period and showing the contributed capital by the partners.
- Statement of partners capital is prepared by them in order to showcase the capital balances of partners and share the earned profit or loss in it (Moehrle, et. al., 2010).
4.3 Interpret the financial statements of the two restaurants using ratios and comparisons, both internal and external.
Calculated ratios are shown below in the table such as: -
Analysis made over the calculated ratios such as:
|
Ratios |
Sweet menu |
Blue Island |
Interpretation |
|
Return on capital employed |
They make adequate use of their employed capital and get return at the rate of 59.48% |
They make adequate use of their employed capital and get return at the rate of 103.09% |
This ratio evaluate the efficiency of organisation to make use of their employed capital. It is interpreted that Blue Island is getting effective returns over their capital employed as their rate of return is nearly double of the rate of return attained by Sweet menu. |
|
Gross profit ratio |
They make effective sales and get returns at the rate of 63.57%. |
They make effective sales and get returns at the rate of 66.22%. |
This ratio shows the revenue earning efficiency of the organisation with the help of their sales. The efficiency of Blue Island in getting revenues is higher than Sweet menu. |
|
Interest cover |
They earn adequate funds in the ratio of 11.6 in order to cover their interest. |
They earn funds in the effective ratio to cover their interest as their ratio is 42.27. |
This ratio helps in getting to know about the efficiency of organisation to recover the interest amount. Blue Island is effective enough as they are getting interest cover 4 times better than Sweet menu. |
|
Current ratio |
They are having adequate level of funds in the ratio of 1.79. |
They are having funds in the ratio of 0.63. |
This ratio shows the efficiency of maintaining adequate funds to meet out their liabilities. Sweet menu is looking quite sufficient as they attain around 3 times better ratio as compare to Blue Island. |
|
Quick asset |
They are having effective level of liquid funds with them as their ratio is 0.63. |
They are having little funds in the ratio of 0.15. |
This ratio shows the efficiency of maintaining adequate liquid funds to meet out their short term liabilities. Sweet menu is looking quite sufficient as they attain around 5 times better ratio as compare to Blue Island. |
|
Debt equity ratio |
They are having short term debts in the ratio of 0.19 as compare to their equity capital. |
They are having short term debts in the ratio of 0.04 as compare to their equity capital. |
This ratio shows the utilisation of the debts in order to run their routinely activities. Blue Island is much effective as they run their routinely activities with the use of their equity funds. |
|
Total debt-equity |
They are having debts in the ratio of 0.42 as compare to their equity capital. |
They are having debts in the ratio of 0.59 as compare to their equity capital. |
This ratio shows the utilisation of the debts in order to run their organisational activities. Sweet menu is much effective as they run their organisational activities with the use of their equity funds in comparison to Blue Island. |
Conclusion: The above interpretation shows that both restaurants having their own speciality such as Blue Island is effective in earning revenues whereas Sweet menu is efficient in maintaining adequate level of funds with them to deal with their activities.
Conclusion
In the end it get concluded that Sweet menu evaluate all available financial sources and as per their requirement they chose bank loan, issue new shares and utilise their saved funds. They make use of their funds with the help of financial planning. Blue Island utilise cash budget to allocate their funds and also use investment appraisal techniques to select the profitable machinery. To measure the effective restaurant among Sweet menu and Blue Island financial ratio analysis is made and according to which Sweet menu is more liquid able and Blue Island is more profitable.
References
Adkins, R. & Paxson, D. 2014, "Stochastic Equipment Capital Budgeting with Technological Progress", European Financial Management, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 1031-1049.
Ahrendsen, B.L. & Katchova, A.L. 2012, "Financial ratio analysis using ARMS data", Agricultural Finance Review,vol. 72, no. 2, pp.
62-272.
Alin-Eliodor, T. 2014, "Financial Statements Analysis",Journal of Knowledge Management, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 62-73.
Baker, H.K. & English, P. 2011;2013;, Capital Budgeting Valuation: Financial Analysis for Today's Investment Projects, 1. Aufl.;1; edn, Wiley, Hoboken.
Barth, M.E., Konchitchki, Y. & Landsman, W.R. 2013, "Cost of capital and earnings transparency", Journal of Accounting and Economics, vol. 55, no. 2-3, pp. 206-224.
Bird, C.L., Sener, A. & Coskuner, S. 2014, "Visualizing financial success: planning is key", International Journal of Consumer Studies, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 684-691.
Blanco, B., Garcia Lara, J.M. & Tribo, J.A. 2015, "Segment Disclosure and Cost of Capital", Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, vol. 42, no. 3-4, pp. 367-411.
Details
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution