- support@locusassignments.com
Structure & Culture Organisations and Behavior Assignment
|
Program |
Diploma in Business |
|
Unit Number and Title |
Unit 3 Structure & Culture Organisations and Behavior |
|
QFC Level |
Level 4 |
Introduction:
The structure & culture organisations and behaviour unit mainly focuses on the organisational structure and culture and their impact on the performance of the organisation. The structure and culture of the organisation refers to the beliefs and values of the organisation. All the rules and principles on which the organisation conducts its processes are based on its culture and structure. Organisation needs to take decisions regarding the approaches and the theories that are to be followed in the organisation. These theories are related to the management practices of the organisation. This unit also describes about the management approaches like scientific, classical and human relation approach. These approaches explain about the concept of leadership. Leadership means guiding employees to work in a specific manner. Leaders not only guide employees but also motivate them. There are many motivational theories like; Maslow hierarchy needs theory, Herzberg two-factor theory, ERG theory etc.
The unit also focuses on the pattern of working of employees. Teamwork is the practice used by many organisations these days. It helps in improving the communication channel and in turn enhances the performance of employees as a team. We will also draw attention towards how technology has its impact on the teamwork in the following unit.
Task 1:
1.1 Compare and contrast different organizational structure and culture.
Not every organization works in the same manner. They differ in their working patterns, their culture, their policies etc. This helps in developing an organization structure. Organizational structure of a company is based on many characteristics.
If we talk about the formal organizational structure, it is categorized as:
- Functional structure: The organization that follows the functional structure are those in which groups are made according to the specific skills to perform a particular function. The employees with particular skills work together for the common goals in particular department.
- Product based: The groups are made according to a particular product in these organizations. Companies that have wide variety of product businesses mainly use such structure. It helps the organisation to work upon multiple product lines simultaneously. (Brooks, 2009)
- Geography based: In these organizations, each department is present under the different regional units of the organization. The organisations have region wise decentralised units. They are formed to serve the specific market or region.
- Multi divisional and multifunctional: This structure is followed by the organization that is competing globally and has the subsidiaries that function as the separate business units. Each subsidiary has its own departmentalisation. (Goldsmith, Baldoni and McArthur, 2010)
- Matrix: It is a complex structure involving the characteristics of both functional and product based structures. The organizations following matrix structures have more than one reporting lines.
There are some of the elements that are required to be followed by the organisation in the organisation structures. First, one is the unity of command or chain of command that suggests that an employee should have one superior who commands him rather than multiple superiors. Another element is the span of control. It refers to the extent of control a manager has with respect to the number of employees in his team. It can be narrow in some organisations and can be wide in others according to the structure of the organisation. (Luthra, 2015)
If we consider CAPCO, it has the flat organizational structure having very few layers of management. This is non-hierarchical structured organisation with wide span of control. CAPCO sometimes uses the matrix structure for the completion of some specific projects. This is in contrast with the organisational structure followed by the traditional bureaucratic organisation such as NHS having a very long hierarchical structure with narrow span of control. (De Cremer, 2006)
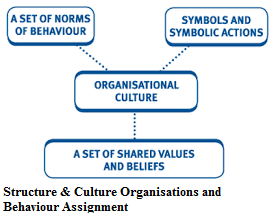
Organisation culture is the beliefs and values of the organisation. It shapes the organisation. Organisation culture can mainly be classified as:
- Power culture
- Role culture
- Task culture
- Person culture
CAPCO is the organisation that provides freedom to the employees to come up with their own creativity to perform tasks and focus on personal growth of themselves. They provide an open environment for their employees to work whereas the organizations like NHS have very different kind of culture. NHS has traditional organizational structure and culture that somehow does not allow the employees to come up with their own ideas of working but they have the culture of teamwork that is also followed by CAPCO.
1.2 Explain how the relationship between an organisation’s structure and culture can impact on the performance of the business.
The relationship between the structure and the culture affects the performance of the organisation. If an organisation is following the traditional hierarchical structure then they should adopt the culture with traditional values to perform towards the goals in better way. If we take example of CAPCO, they follow the flat organisational structure with fewer layers of management that somehow provides the organisation with an ease to communicate which in turn leads to efficient teamwork. CAPCO believes in creativity and allows their employees to come up with their own ideas of work. (Millar, 1979)
The values of creativity, integrity and involvement of employees are the main reason that CAPCO’s growth rate is 14.7%, which is far more than its competitor’s growth percentage. As CAPCO has the flat organisational structure, it is very easy for the employees to communicate with the top management that creates a sense of belongingness in the employees. This motivates employees to perform better. Their involvement in decision making process is also one of the motivational factors that leads to better performance of employees and in turn affects the success of the organisation as a whole. The company has also made efforts to enhance inter employees communication by introducing a social media application called Capln Touch. This positive approach towards communication also leads to personal growth of individuals as well as affects the organisational performance. (Ordway and Claudin, 1987)
1.3 Discuss the factors, which influence individual behaviour at work.
In any organisation, the behaviour of an individual at work is influenced by organisational as well as personal factors. Organisational factors include the culture of the organisation, working environment etc and personal factors includes personality, designation, background of that individual etc. Let us understand it better by taking an example of CAPCO. (Capco.com, 2016).
Organisational factors:
- Culture: CAPCO believes in creativity and innovation so the employees working thereare allowed to come up with their own ideas of working that gives them a sense of belongingness and it reflects in their performance in a positive way.
- Working environment: The working environment of CAPCO is very much open and free. They provide stress free environment to the employees working there. If an employee works without stress, it enhances their performance and they behave in a very positive manner towards the organisation.
- Personal factors: Personality: Personality refers to the inherent traits of an individual that differs from person to person. The behaviour of a person is highly influenced by the personality. Suppose if a person is introvert than he may resist himself to initiate things and may fail to express his views in front of others.
- Designation: The employee at higher designation definitely has different behaviour than the employees at executive level because they have to maintain that decorum of the organisational hierarchy system.
- Background: Cultural background of an employee is one of the main reasons that influence the individual behaviour at work. For example, the worker from London behaves differently from the Irish worker working in the same organisation. (Millar, 1979)
Above all are some of the factors that somehow influence the behaviour of individuals. Even if the organisational culture is same for every individual in the company, they behave differently according to their different individual traits.
Contact us
Get assignment help from full time dedicated experts of Locus assignments.
Call us: +44 – 7497 786 317Email: support@locusassignments.com
Order Now!!
Task 2:
2.1 Compare the effectiveness of different leadership styles in different organizations.
Leadership can be defined as the capability of a person to influence someone to work in a particular manner. It is the ability to guide and mentor others to perform towards a specific goal in a specified way. As we know that, the different individuals respond to the same stimulus in different way and it makes their personality. Leadership is also a part of an individual’s personality and have different styles.
If we classify the leadership, it can be categorized mainly in three styles:
- Democratic: The leaders who follow democratic leadership styles believes in considering the views of group members in the decision making process. The final decision remains in the hands of the leader but he definitely allows the group members to come up with their views regarding the issue on which the decision has to be taken. (Schmid, 2006)
- Authoritative or autocratic: This is the type of the leadership under which all the power of decision making remains in the hands of the leaders without the consent of the group members. He takes the decision on his own and communicates it to others that need to be accepted by the group even if they do not agree with it. (Thorpe, 2008).
- Laissez faire style: Under this style of leadership, group members are free to take their own decisions. Leaders only behave as the guide and the group members take the final decision only.
Comparison of CAPCO leadership style with Sainsbury:
CAPCO
Leadership style: democratic
As we know that CAPCO has a very open work culture and they believe in creativity and innovation that shows that the leaders of CAPCO follows the democratic style of leadership. They consider the opinion of their employees before taking any decision. With the great communication channel, it is very easy for the employees to connect with the leadership teams. (Capco.com, 2016).
Sainsbury
Leadership style: laissez faire
Unlike CAPCO, Sainsbury follows the laissez faire leadership style. They believe that with this style they can rely upon the employees to take decisions effectively. (J-sainsbury.co.uk. , 2016)
|
Democratic style by CAPCO |
Laissez faire style by Sainsbury |
|
CAPCO allows partial involvement of employees |
Sainsbury leaders depends solely on employees |
|
CAPCO employees are guided by leaders |
Sainsbury hire highly skilled employees |
|
Employees share opinions |
Employees make decisions |
|
CAPCO leaders give regular feedback to their employees |
Sainsbury leaders do not provide regular feedback |
2.2 Explain how organisational theory underpins the practice of management.
Organizational theory refers to the design of organization. It includes the organizational structure, culture and their relation with the external environment. It forms the basis of the practices of the management. It guides the managers to plan over the things and suggest ways to respond to any stimulus. Organisational theory suggests the rules on which the organization runs and it gives the foundation to the management practices. (Brijesh Goswami, 2013).
Following are some of the organizational theories that affect the management practices of the organization:
Classical management theory: This theory deals with the organization that are formal in nature. It focuses on analysing the organizational structure. This includes two types of management approaches-
- Scientific approach
- Bureaucratic approach
Scientific approach of management is about standardisation. It deals with increased productivity by using standard and scientific tools and making a proper structure of the processes to be done. An organization with this approach believes in scientific selection of employees, proper training and development as well as dividing the labour in such a way that leads to efficient working of the employees and the organization as a whole.
Bureaucratic approach also deals with formal organizations in which jobs are very much specific and the organization that follow this approach have authoritative kind of leadership in which employee involvement is negligible.( Lerner, Miodownik and Lerner, 2015)
Neo classical approach: Now the classical approach is renewed as the neo classical approach with some modifications. This approach focuses on individuals and human relations. The organization with this approach has participative or democratic leadership style. This theory or approach supports the concept of work groups.
Modern approach: With the change in the environment, the organizations felt the need to make changes in the management approaches they use. Modern approach of management came into picture now.
It involves two approaches;
- System approach
- Contingency approach
System approach includes both the concepts of strategic working as well as the human behaviour. This approach considers an organization as the system having interrelated processes.
Contingency approach is the modified form of system approach. The organization following this approach believes that there should be no specific system for the organization to run. The response depends on the stimulus that means that the approach used in the organization totally depends on the situation at that particular time. Organization processes cannot be conducted in the same manner in all situations. (Brijesh Goswami, 2013)
2.3 Evaluate the different approaches to management used by different organisations.
Different organisations use different approaches for management. It depends on the culture and the values followed by the organisation. The organisation which focuses on individuals generally follow human relation approach and the organization having their focus on productivity will definitely go for the classical approaches like scientific and bureaucratic.
CAPCO
Management approach: contingency
The management approach followed by CAPCO is contingency approach. As CAPCO is the organization that believes in change management, contingency approach is the best to be followed by them. They have their change management consultants who guide them according to the dynamic environment inside as well as outside the organization. (Capco.com, 2016).
Sainsbury
Management approach: neo classical approach
Sainsbury is an employee-focussed organisation. They provide opportunities to their employees to develop their skills and knowledge. Reward system is practiced in the organisation. Employees are rewarded according to their performances. This in turn motivates the employees to perform better. (J-sainsbury.co.uk., 2016).
|
Neo classical approach by Sainsbury |
Contingency approach by CAPCO |
|
Focussed on human relations |
Focussed on change management |
|
Guidelines suitable for employees |
Guidelines suitable for all situations |
|
Policies are made according to the workforce |
Policies are made according to dynamic environment |
Task 3
3.1 Discuss the impact that different leadership styles may have on motivation in organisations in periods of change.
Leadership is the ability of an individual to influence employees or group members to work in a particular manner. Leadership styles adopted by the organisation not only depend on the leaders but also depend upon the group members who are governed by them. The culture and organisational structure also influence the leadership style adopted by the organisation. Leaders not only influence employees but also motivate them towards a specific goal. Effective and efficient utilisation of human resource can only be done by motivating them. Leadership style has an impact on the motivation of the employees. (Luthra, 2015)
Motivation is the stimulating factor that causes an individual to work in an effective manner towards a particular goal and the result of the motivation factor reflects in the performance of the employee. Every individual has different motivational factors.
Two aspects of leadership have their influence in motivating employees.
- Persuasive leadership
- Participative leadership
Persuasive leadership is about influencing employees upon the decision that has already been made by the leader. Under this style of leadership, leaders try to motivate employees according to their will. Leaders try to make up the minds of the employees in the way the decision has been made.
Participative leadership is about considering employees knowledge and opinions before taking the decision regarding any issue. The involvement of employees in the decision-making process is the motivation factor for the employees. (De Cremer, 2006)
Motivation depends on the needs of the employees. As the time changes, the needs of the employees also change and hence change the factors, that motivates them for better performance. Different motivational theories have been proposed to understand the above concept.
3.2 Compare the application of different motivational theories within the work place.
Maslow hierarchy needs theory: This theory states that the needs of an individual changes with time and there is a pattern in which the needs are arranged. One need follows the other and so on. An individual cannot be motivated to achieve higher-level need until he has achieved the lower level needs. (Teater, 2010)
Maslow hierarchy needs theory involves five levels:
- Physiological needs
- Safety needs
- Belongingness needs
- Esteem needs
- Self-actualisation needs
- Physiological needs: These are the most basic needs of an individual that includes air, water, shelter, food etc. In terms of the job of an individual, the basic need of an employee is the basic salary.
- Safety needs: After the fulfilment of physiological needs, employees start working towards safety needs that includes security of job, safe environment to work, health insurance etc.
- Belongingness needs: These needs include love, affection, care, communication between the employees and support from the superiors. These are very important as humans are social animals and cannot work without the support of other human beings. That support could be emotional or mental. (Heinrichs, Oser and Lovat, 2013)
- Esteem needs: As the above three needs of an individual are achieved, now he tries to achieve and make efforts to achieve the esteem needs that includes recognition, high status and promotion.
- Self-actualisation: fter achieving all the above stated needs, now it is time to achieve the needs that develops a sense of self-satisfaction in an individual’s mind. Self-actualisation needs include growth and creativity.
Application of Maslow hierarchy needs theory within workplace:
Maslow theory can be applied in the workplace with the help of the leaders as well as the employees. As this theory is about the hierarchy of the needs, the employees and the managers, both have to put efforts systematically. For achieving the basic physiological needs, managers need to guide the employees and employees need to do the delegated task on time without compromising with the quality of work. (Mcreynolds,2012).
- For achieving the safety needs, organisation must provide a safe environment to all the employees.
- Social needs of an employee can be fulfilled by bringing them together in meetings and allow them to communicate freely.
- After the achievement of social needs, employee wants to be recognised for the good work he is doing. This recognition and status needs can be achieved only if managers ensure them that they are important for the organisation.
- Last, is the self-actualisation need. This is the level at which employees are satisfied with what they have earned and they have the feeling of self-satisfaction in them. (Teater, 2010)
Herzberg two-factor theory:
Frederick proposed this theory called Herzberg two-factor theory. The name suggests that it involves two factors, which are:
- Motivators
- Hygiene factors
Motivators are factors that motivates and inspire an employee to perform better. For example, rewards, recognition, awards etc. These factors are present to satisfy employees.
Hygiene factors are those that are present to avoid the dissatisfaction of the employees. Like salary, work conditions etc. They cannot give a positive satisfaction but can be a cause of dissatisfaction if not present.
Application of Herzberg theory:
Every employee of the organisation can be satisfied or dissatisfied. This theory says that motivation and hygiene factors are equally important for an employee. Hygiene factor can prevent the dissatisfaction buy motivation factors can provide satisfaction to the employees. The theory can be applied by designing a job in such a way that can fulfil the basic needs of the employees and simultaneously provide him the chance to achieve other physiological and esteem needs. (Rudolph, 2016)
3.3 Evaluate the usefulness of a motivation theory for managers.
There are many motivational theories that are introduced for the organisations. The application of these theories has utmost importance in the organisations to motivate and inspire employees to perform in an effective way. It is very necessary for managers to understand the usefulness of motivational theories. The main function of managers is to make human resource work in an efficient way. Managers have to provide the path according to which the employees work. There exists a give and take relationship between the employee and the organisation. The employees work for the organisation and the organisation pay them accordingly. However, to compete with the competitors and to deal with the dynamic environment the organisation needs to increase its efficiency to perform. This increase in the performance of organisation can be achieved only when its employees work in an efficient way. The need to increase the efficiency leads to the introduction of motivational factors in the organisation to inspire employees to work. The growth of the organisation and the employees run hand in hand. If the organisation is growing then it will definitely affect the growth of employees in a positive way. (De Cremer, 2006)
It is the duty of the manager to motivate employees to perform. The introduction of reward system for the efficient workers creates a sense of competition between the employees and they work more efficiently. If we talk about the Maslow needs theory, it suggests that human needs change with time and they have hierarchical system. If the basic needs are fulfilled than humans start working towards the achievement of higher-level needs and so on. Managers have to recognise the level of needs of an employee and motivate them accordingly.
If we consider Herzberg theory of motivation, it suggests that satisfaction of the employees is important but avoiding the dissatisfaction is equally important. So the employees should be provided with some hygiene factors such as healthy work conditions etc. It helps in preventing dissatisfaction of working in the minds of the employees. (Ordway and Claudin, 1987)
Task 4
4.1 Explain the nature of groups and group behaviour within organisations.
When two or more people come together for any particular purpose, they form a group. In the case of organisations, the collection of employees who are working towards a common goal forms a group. (Frazer and Oswald, 2009)
- Nature of group:
- Formal group
- Informal group
Formal group: Groups that include the specially designated employees working for the achievement of the specific purpose are known as formal groups. The managers without the concern of the group members choose the members in these groups deliberately. These groups can be permanent or temporary according to purpose of formation of group. (Gregory, 2013)
Informal groups are formed according to the willingness of the member to join the group. They do not have a definite purpose. They are either friendship groups or interest groups.
Most of the organisation forms the work groups to solve a particular problem or to achieve a specific goal. Working in a group has many benefits for the employees as well as for the organisation. Some of the benefits are:
- Improved communication channel
- Involvement of employees
- Synergy
- Exchange of opinions
- Sharing of knowledge and skills
- Early completion of task
As far as CAPCO is concerned, forming work groups is the common practice in the organisation. They generally form the temporary formal groups who work for the common purpose. After completion of that particular task, they dissociate the group. CAPCO is employee driven organisation where employees have the freedom to share their opinions and views regarding any issue in the organisation. As the organisation has a open working environment, employees easily communicate with each other and can work as a team.
Working in a group dissociates the responsibilities and the burden and enhance the efficiency of performance.
4.2 Discuss factors that may promote or inhibit the development of effective teamwork in organisations.
Human being is a social animal. He needs a society to live. If we talk about the organisations, same concept is applied. Employees working individually may not perform well as compared to the performance they give when they work in a group. Many factors can affect the performance of the team. Some factors promote the teamwork and some may inhibit them. (Gregory, 2013)
Factors promoting team work:
- Diversity: diversity in culture, personality and behaviour leads to innovation and creativity. Employees belonging to diverse culture and personality generate better ideas by sharing their views.
- Communication: better communication leads to better performance. If there is good communication between the employees, than they can share the knowledge and opinions effectively and can reach to the conclusion very early.
- Leadership: great leaders form the great teams. The skills of leaders affect the performance of the team as a whole.
- Team size: the appropriate team size is very necessary for the effective teamwork. Very large team may create chaoSynergy: bond between the members should be strong to perform effectively.
Let us take an example of the organisation called CAPCO.
CAPCO believes in teamwork rather than individual work. The reason behind the CAPCO’s effective teamwork is the social behaviour of the employees. CAPCO has the great communication channel that leads to effective performance of the teams. The leadership approach followed in CAPCO is democratic, where employees are involved in the process of decision-making, this develops synergy between the employees as well as between the employees and the organisation. (Capco.com, 2016).
Factors inhibiting team work:
- Unclear goals: If employees are not clear with the responsibilities and goals, it can affect the performance of the team as a whole.
- Poor communication: Poor communication leads to ineffective working environment, as there is lack of information sharing between the employees.
- Lack of managerial involvement: Manager’s guidance and involvement is very necessary for the effective performance of the team. (Frazer and Oswald, 2009)
CAPCO is an organisation with an open working environment. They practice teamwork as the method to enhance performance of the organisation. As we know that CACPO has a democratic kind of leadership in which employees are involved in the decision making process. This can sometime act as a drawback for the teamwork as there is less involvement of managers. (Ghaferi, Dimick, 2015).
4.3 Evaluate the impact of technology on team functioning within a given organisation.
We are very much aware with the technology advancement across the globe. Technology has become a part of daily lives. Technology plays a very vital role in the industries like, IT, financial institutions, marketing etc. Technology has reduced the manual work. Technology has an immense importance in the organisation like CAPCO, which is a financial service firm.
CAPCO is using technology in the following form:
- Social media: It uses LinkedIn as the medium to communicate the benefits of the associate talent programme.
- CaplnTouch: Employees of CAPCO working at different location can communicate with each other using this application. This helps in information sharing between the employees and provides them with opportunities to share their entrepreneurial ideas.
There are many other forms in which technology can be used to enhance the team work.
Some of them are:
- Websites: websites are the collection of webpage on the internet where all the information about the organisation has been given. CAPCO owns its website on the internet where the information about the company is shared with users. This website is available for all the users who can access internet.
- Intranet: intranet is the facility of connecting employees within an organisation through an electronic medium.
- Virtual teams: Technology is very important for the organisation to work in an efficient and effective manner. It helps in increasing the pace of work. Technology has a very positive impact on the teamwork. With the use of technology virtual teams can be formed. The employees working at different location been exposed to each other and forms a virtual team to work towards a common goal with the help of electronic mediums and web. (Ghaferi, and Dimick, 2015).
Conclusion:
The structure and culture has a great impact upon the functioning of the organisation. Different organisations have different work patterns according to their culture and structure. Organisation is classified according to the functions, geographic region and product lines. Different organisation use different management practices and approaches such as; classical that includes bureaucratic and scientific approach, neo classical that includes human relation approach and modern that includes contingency and system approach.
Different motivational and leadership theories are followed by different organisation. Motivational theories like Maslow hierarchy needs theory, Herzberg theory etc and leadership styles like democratic, autocratic etc are followed by the organisation according to their principles and policies.
Now days, organisations are adopting the culture of teamwork as it enhances the performance of the employees and the organisation as a whole.
References:
Books:
Brooks, I. (2009). Organisational behaviour. Harlow, England: Prentice Hall/Financial Times.
Goldsmith, M., Baldoni, J. and McArthur, S. (2010). The AMA handbook of leadership. New York: American Management Association.
Teater, B. (2010). An introduction to applying social work theories and methods. Maidenhead, England: McGraw-Hill/Open University Press.
Heinrichs, K., Oser, F. and Lovat, T. (2013). Handbook of moral motivation. Rotterdam: SensePublishers.
Mcreynolds, J. (2012). Motivational theories & psychology. Delhi: English Press.
Frazer, R. and Oswald, P. (2009). Teamwork!. New York: Simon Spotlight.
Journals:
De Cremer, D. (2006). Affective and motivational consequences of leader self-sacrifice: The moderating effect of autocratic leadership. The Leadership Quarterly, 17(1), pp.79-93.
Luthra, A. (2015). P-143: Classification of behaviors in dementia based in ”motivational” and ”needs based” theories. European Geriatric Medicine, 6, p.S70.
Ordway, F. and Claudin, M. (1987). Building the organisation: Structure, programmes and activities. Acta Astronautica, 15(10), pp.779-805.
Schmid, H. (2006). Leadership styles and leadership change in human and community service organizations. Nonprofit Management Leadership, 17(2), pp.179-194.
Thorpe, R. (2008). Introduction: Constructionist Approaches to Management Research. Management Learning, 39(2), pp.115-121.
Lerner, P., Miodownik, C. and Lerner, V. (2015). Tardive dyskinesia (syndrome): Current concept and modern approaches to its management. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 69(6), pp.321-334.
Need Help with Your Assignment?
Get expert guidance from top professionals & submit your work with confidence.
Fast • Reliable • Expert Support
Upload NowDetails
Other Assignments
Related Solution
Other Solution



